The nervous system represents a communication network of the organism .
It is formed by a set of organs of the human body that have the function of capturing messages, stimuli from the environment , “interpreting them” and “archiving them”.
Consequently, he elaborates responses , which can be given in the form of movements, sensations or findings.
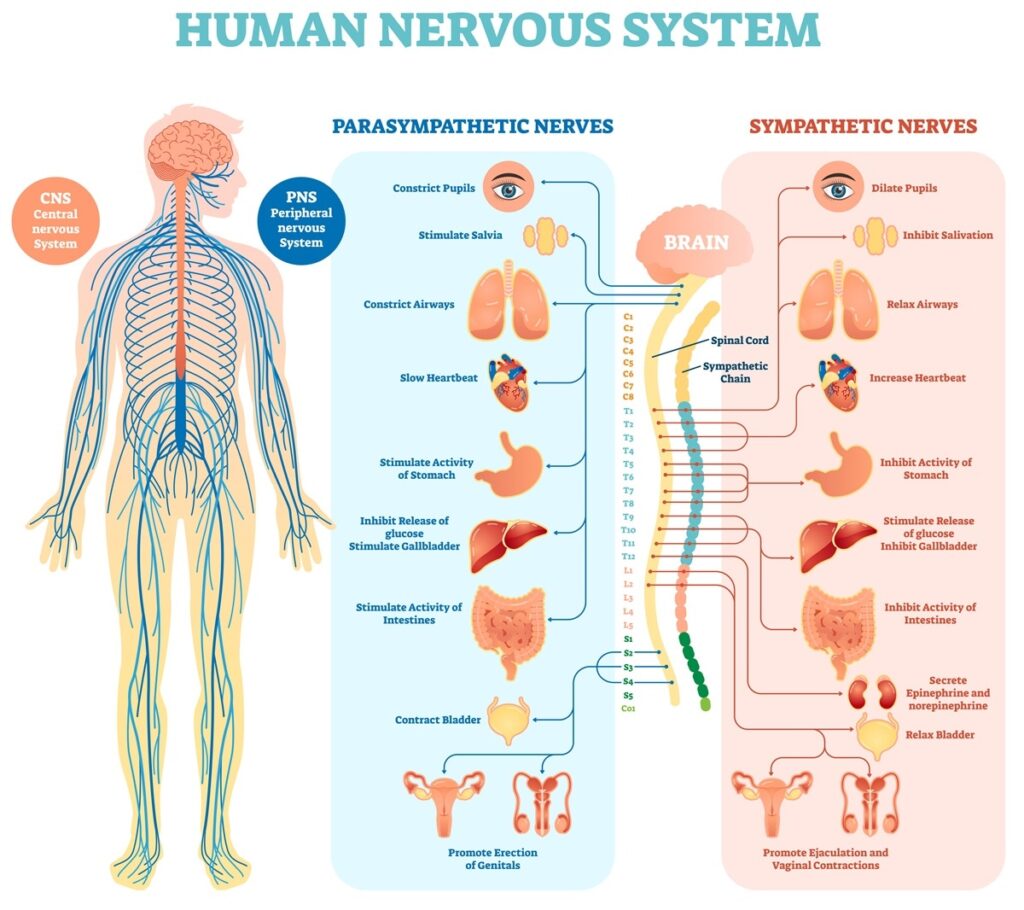
The Nervous System is divided into two fundamental parts : central nervous system and peripheral nervous system
Central Nervous System
The Central Nervous System consists of the brain and the spinal cord , both involved and protected by three membranes called meninges .
Brain
The brain , which weighs approximately 1.5 kilos, is located in the cranial box and has three main organs : the brain, the cerebellum and the brain stem;
Brain
It is the most important organ of the nervous system. Considered the most bulky organ, as it occupies most of the brain, the brain is divided into two symmetrical parts: the right hemisphere and the left hemisphere .
Thus, the outermost layer of the brain and full of recesses, is called the cerebral cortex , responsible for thinking, seeing, hearing, touching, tasting, speaking, writing, etc.
In addition, it is the seat of conscious and unconscious acts, memory, reasoning, intelligence and imagination, and it also controls voluntary body movements.
Learn more about the Brain .
Cerebellum
Located at the back and below the brain, the cerebellum coordinates the precise movements of the body, in addition to maintaining balance . In addition, it regulates muscle tone, that is, it regulates the degree of contraction of muscles at rest.
Brain Stem
Located at the bottom of the brain, the brainstem conducts nerve impulses from the brain to the spinal cord and vice versa.
In addition, it produces the nervous stimuli that control vital activities such as breathing movements, heartbeat and reflexes , such as coughing, sneezing and swallowing.
See also : Brain
Spinal cord
The spinal cord is a cord of nerve tissue located within the spine . At the top it is connected to the brainstem .
Its function is to direct nerve impulses from the rest of the body to the brain and coordinate involuntary acts (reflexes).
Peripheral Nervous System
The peripheral nervous system is formed by nerves that originate in the brain and spinal cord.
Its function is to connect the central nervous system to the rest of the body. It is important to note that there are two types of nerves: cranial and spinal nerves .
- Cranial nerves : they are distributed in 12 pairs that leave the brain, and their function is to transmit sensory or motor messages, especially to the head and neck areas.
- Spinal Nerves : 31 pairs of nerves that come out of the spinal cord. They are formed of sensory neurons, which receive stimuli from the environment; and motor neurons that take impulses from the central nervous system to the muscles or glands.
According to its performance , the peripheral nervous system can be divided into somatic nervous system and autonomic nervous system .
- Somatic Nervous System : regulates voluntary actions, that is, which are under the control of our will as well as regulates the skeletal muscles of the entire body.
- Autonomic Nervous System : acts in an integrated manner with the central nervous system and has two subdivisions: the sympathetic nervous system, which stimulates the functioning of the organs, and the parasympathetic nervous system which inhibits its functioning.
In general, these two systems have opposite functions . While the sympathetic nervous system dilates the pupil and increases the heart rate, the parasympathetic , in turn, contracts the pupil and decreases the heart rate.
Finally, the function of the autonomic nervous system is to regulate organic functions, so that the internal conditions of the organism remain constant.