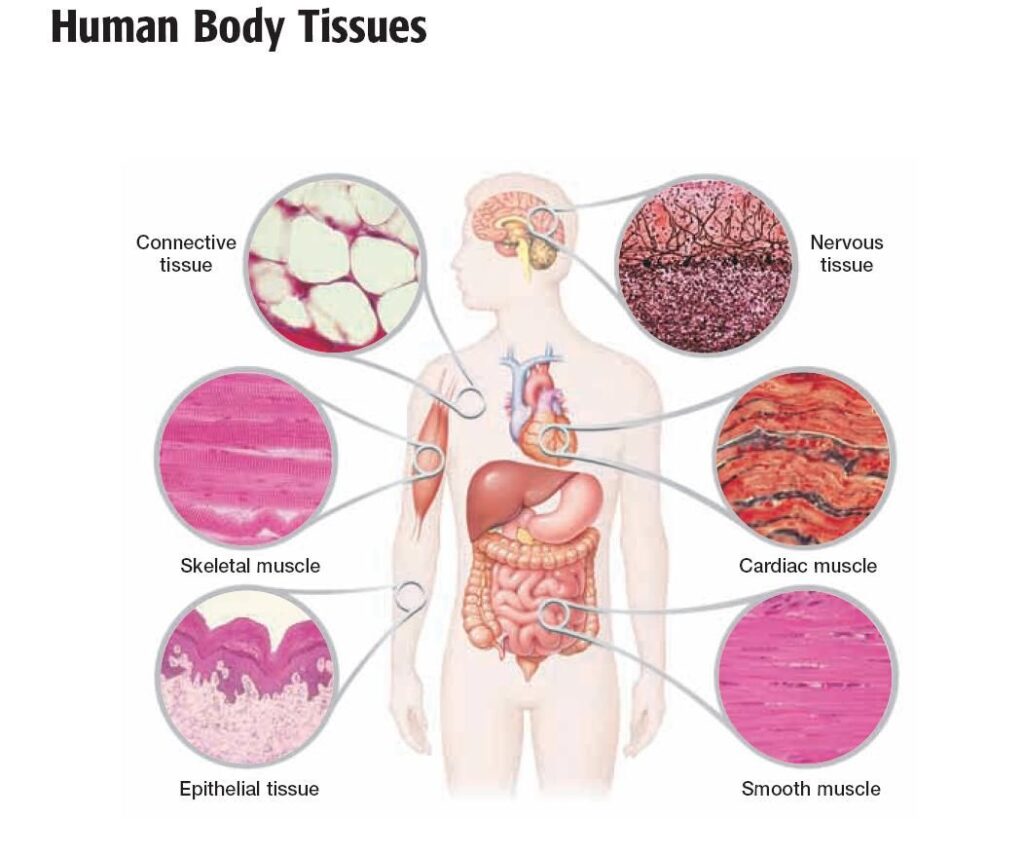
The human body is formed by 4 types of tissues : epithelial, connective, muscular, nervous. It is worth remembering that tissues are formed by the grouping of different cells, each with its function.
Types of Fabrics
The human body is composed of four types of tissue , namely, epithelial tissue , connective tissue (adipose, cartilage, bone , and blood), muscle tissue (smooth, skeletal and cardiac) and nerve tissue .
Epithelial Tissue
The functions of epithelial tissue are body lining, sensitivity and secretion of substances. Therefore, this type of tissue is composed of a group of cells juxtaposed in different shapes: cylindrical, flattened or cubic.
It is interesting to note that in the epithelial tissues there is no presence of blood vessels. A notable example of epithelial tissue is human skin, formed by the epidermis (epithelial tissue) and the dermis (connective tissue).
Connective tissue
The connective tissue has the functions of supporting, filling and transporting substances; its fibers are formed by two types of proteins: collagen and elastin .
So that its cells are well diversified in terms of shape, size and functions, the connective tissue is divided into:
- Adipose Tissue : Composed of adipose cells that accumulate fat (adipocytes), this type of tissue has the main function of thermal insulation of the body, thus being the largest body deposit of energy. From this, it is enough to note that a thin person feels colder than a fat person, since he has more fat tissue than the other (thin) person.
- Cartilaginous tissue : It has a firm, yet flexible consistency; its function is support and lining, for example, the ear, the nose, the trachea. In addition, cartilage cushions the impact of movements on the spine.
- Bone tissue : Rigid tissue, rich in mineral salts, calcium and collagen which makes bones rigid and resistant. In addition, it is innervated and irrigated by blood, its main function being the support of the body, since it makes up the human skeleton .
- Blood Tissue : Formed by several types of cells, this tissue has the body’s defense and nutrient transport functions. It is worth remembering that blood is a liquid tissue, composed of red blood cells , leukocytes , platelets and plasma .
Muscle tissue
The muscle tissue is composed of elongated cells in specialized contraction (contractile proteins: actin and myosin); present great innervation and vascularization, and are divided into:
- Smooth muscle tissue (non-striated): Characterized by involuntary movements, its name corresponds to the absence of transverse streaks, examples are the uterus, bladder and intestine.
- Skeletal muscle tissue : It receives this name, because most of that tissue is next to the skeleton; it has long cells, presence of transverse streaks and voluntary movements.
- Cardiac muscle tissue : Found in the heart, this type of tissue has involuntary movement being formed by long, cylindrical cells in addition to having transverse streaks.
Nervous Tissue
The nerve tissue is mainly made up of nerve cells called neurons . It has long, starry cells that have the ability to transmit nerve impulses. Examples are nerves, the brain and the spinal cord.
Curiosity
The histology is the science that studies the tissues.