The success of the female sexual act depends on both psychological stimulation and local sexual stimulation.
Stimulation

Erotic thoughts can provoke sexual desire in women ; This notably helps the performance of the female sexual act. This desire is highly dependent on your education, as well as your physiological drive, although sexual desire increases in proportion to the level of secretion of sex hormones . The desire also varies according to the sexual cycle and peaks around the time of ovulation, probably due to the high level of estrogen secretion during the ovulatory period.
Local sexual stimulation for women is roughly the same as for men , as massage and other types of stimulation of the vulva , vagina, and certain regions of the perineum create sexual sensations. The glans of the clitoris is especially sensitive to initiate these sensations.
As in the male, sexual sensations are transmitted to the sacral segments of the spinal cord through the pudendal nerve and the sacral plexus. Once these signals have penetrated the spinal cord, they are transmitted to the brain . Also the local reflexes integrated in the sacral and lumbar spinal cord are, in part, responsible for some reactions in female sexual intercourse.
Female erection and lubrication
Around the introitus, extending towards the clitoris , there is erectile tissue almost identical to the erectile tissue of the penis . Like that of the male member, this tissue is controlled by parasympathetic nerves that are directed, through the erector nerves, from the sacral plexus to the external genitalia.
In the early phases of sexual stimulation, parasympathetic signals dilate the arteries of the erectile tissues, probably as a result of the release of acetylcholine , nitric oxide, and vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP) at nerve endings. This allows a rapid accumulation of blood in the erectile tissue, so that the introitus tightens around the penis during penetration; This in turn greatly helps a man to achieve sufficient sexual stimulation for ejaculation to occur.
Parasympathetic signals are also directed to the Bartholin glands, located under the labia minora, to cause mucus secretion immediately inside the introitus. This mucus accounts for a good part of the lubrication during intercourse, although the vaginal epithelium also secretes a lot and a small part of the male urethral glands .
Lubrication is necessary to establish a satisfactory massage sensation during intercourse at the site of irritation, which can occur if the vagina is dry. The perception of massage is the optimal stimulus to provoke the pertinent reflexes that culminate in the masculine and feminine climax.
Female orgasm
When the local stimulation reaches a maximum intensity and especially when the local sensations are supported by adequate signals of psychological conditioning of the brain , they restart reflexes that produce the female orgasm , also called climax.
The female orgasm is analogous to male emission and ejaculation, and perhaps helps promote fertilization of the ovum . The intense sexual sensations that develop during orgasm also target the brain and cause great muscle tension throughout the body. But after the completion of the sexual act, this gives way, in the following minutes, to a feeling of satisfaction characterized by a placid relaxation, an effect called resolution.
Clitoral or vaginal orgasm
Any orgasm requires sufficient stimulation, in intensity and time , of the orgasmic platform ( clitoris , hood and labia minora). Whoever dedicates their efforts to a specific part (clitoris, labia minora …) will achieve orgasm. Whoever incites the platform indirectly (massaging the labia majora, stirring the mons pubis, squeezing the thighs, squeezing the entire pubis on a cushion, or on a teddy bear, or on the partner’s leg, will arrive the same.
During the sexual act, proper, orgasm is more difficult. It requires the bodies of the two contestants to squeeze, pubis to pubis, so that the orgasmic platform is satiated with tightness. It is also possible for skilled women to reach orgasm during intercourse simply by tightening the muscles of the thighs and rectum. Some lucky ones (few) have orgasms only with mental excitement.
Conditions to achieve female orgasm
Stimulation in the right place
The right place can be anyone who directly or indirectly presses on the orgasmic platform:
Clitoris , clitoral hood and labia minora . All these areas have a similar sensitivity when receiving sexual stimuli. Its importance is reflected in the fact that more than 80% of women who masturbate, do so by stroking these specific parts.
In masturbation , women move one or two fingers gently and rhythmically over sensitive areas, or apply rhythmic or constant pressure with multiple fingers or the whole hand.
It is normal for one or two fingers to operate between the labia minora, rubbing along to reach, with each movement, to the clitoris or its base. It is also useful to press the lips between thumb and forefinger, rhythmically.
In some women, these areas are excessively sensitive. In these cases, they tend to prefer stimulation through the clitoral hood, that is, “from above.” Or, stimulation through the mons pubis, the part immediately above the vulva , covered by pelvic hair.
All these structures are linked to the clitoris in its anterior and upper part, and therefore, its stimulation acts indirectly on that organ. Another technique, on these same areas, is the application of the stimulus with an object instead of the fingers.
Major lips . Pressure on the labia majora can be very stimulating for some women. In any case, the normal thing is that, when acting on the labia majora, the force is generally exerted on the entire genital area.
Thigh pressure . It is a masturbation technique used by ten percent of women. The pressures affect the entire genital area (labia majora, minora, clitoris …).
Muscle tensions . There are wonderfulfemale orgasms produced solely by the tension of the muscles in the pelvic area. A prone female, rhythmically moving her buttocks forward and against each other, can climax relatively easily. Some of them take the opportunity to gently press their genitals against the bed, a cushion or a stuffed animal.
The movements of the buttocks, with considerable tension of the gluteal and abductor muscles, imitate the movements of the male during the sexual act, and are the same that the woman performs when she is placed on top in said act.
As a masturbation technique it is not as frequent as others; it reaches five percent of women; But those who experience it say that it is one of the most rewarding in terms of the quality of orgasms achieved.
The breasts . In many women, the breasts, and especially the nipples, are erotically sensitive. The stimulation of the breasts, by itself, is not enough to reach orgasm, except in some very sensitive women. But it is very useful to combine the stimulation of the breasts (caressing them, pressing them with the hand or the body, kissing them …) with that of the genitals.
The Vagina . The reality is that there are only erogenous zones in the initial part of the vagina. Further inside, the equipment for “pleasure terminals” is scarce or non-existent. Hence, although around 20% of women masturbate by inserting fingers or objects into the vagina, few of them stop stroking the rest of their genitals at the same time.
Some women have a sensitive so-called G-spot (after its discoverer, Grafenberg). It is, more or less, the area of the vagina corresponding to the clitoris, below. To reach it, a finger, preferably the middle, must be inserted into the vagina. With the ball of the finger pointing up, this point can be stimulated. Not all women react in this room. The most practical is to test, ask, and act accordingly.
Stimulation the right way
The proper form is the one that each woman considers suitable for herself. If the woman is experienced in masturbating, it is best to tell the man how she does it, or to give a practical demonstration.
There are women who prefer stimulation with the fingers, others with the tongue, others select the rubbing of the genitals with the partner’s body. Vibrators and telephone showers (plus the latter) are a source of comfort for many women. They can also be used in a relationship.
The sexual act, itself, can be an appropriate way, if the woman has learned to reach orgasm by pressing against the man’s body in each movement of the penetration and exercising the muscular tensions mentioned above. In the opposite case, the sexual act, itself, is one of the most tiring and inoperative ways for women to reach the fascinating and restorative orgasm.
Stimulation for the necessary time
It is normal for a woman, masturbating alone, to reach orgasm in relatively short periods of one to five minutes. But that same woman, in a sexual relationship with a partner, can take between fifteen and thirty minutes to reach the delicious ending.
This is due to the importance of the psychological component. In solitary masturbation, the psychological component is easy to control by the woman herself. Many women, a third at least, do not have erotic fantasies during masturbation . On the other hand, in men, fantasies appear in one hundred percent.
The psychological component in women is not necessarily sexual or erotic in nature. The readings used by men when masturbating are, with great preference, those of a pornographic type. Instead women prefer romance novels.
Another circumstance that delays obtaining orgasm in company is the desire to prolong the act (to enjoy it longer ). Unfortunately, most of the time that the female orgasm is delayed, it is due to the ineffectiveness of the techniques that couples use regularly in intercourse.
Stimulation with the appropriate psychological components
The psychological components in female sexuality are much less sexual than those of the male. The man reacts readily to sexual stimuli, while the woman is calmer in her reaction. For women, the most important thing is to feel relaxed, calm, secure. If they see urgencies in the male, they can be blocked when they perceive that they do not vibrate with the same speed or ease.
Therefore, when we speak of psychological components we are not referring to sexual or erotic components. The well-known period of preparation in which couples caress each other, before the sexual act, is not for the woman, a period of sexual preparation, but a way of transmitting affection and non-demanding sex.
Dating couples, in the classic way, are experienced in periods of caressing and kissing before reaching the most intimate sexual relationship. It is even common that caresses, in the long run, include the breasts and genitals. Such caresses (what in English is known as “peeting”), without orgasm or with orgasm, usually coincide with phases of great affection and passion. Hence, they tend to be very satisfactory and desired by both members of the couple.
But when more time is available, along with the problems that coexistence entails, the caressing phases can be shortened, which does not favor things by disturbing the necessary relaxation of the woman. In such circumstances, women find quick or overt approaches unpleasant.
One orgasm or several?
Women have the ability to have multiple orgasms in a single session. Most of them are satisfied with a single orgasm , but could be re-aroused by lacking a refractory period.
In some of them, orgasmic contractions are produced in numbers much higher than the twelve that we mentioned before as common. When speaking of these experiences they can cite “repeated orgasms, up to more than a hundred”. It is likely that it is a single orgasm, although – yes – very long and ostentatious.
Phases in the female sexual act
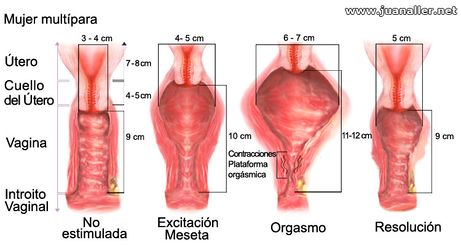
Excitation phase
When the woman, in the right psychological conditions, begins to become sexually aroused, changes appear in the breasts and genitals. The breasts increase in size, globally, and the nipple stands up.
The sexual reddening of the skin arises , which in this phase turns a deep pink color; especially from the part of the stomach and breasts breasts .
Voluntary muscle tension is applied, especially in the abdomen and chest areas .
In the genitals a slight expansion of the vaginal wall is noted, and, between 10 and 30 seconds after the onset of arousal, the glands of the vagina secrete lubricating fluid. This sensation of “being wet” is the first that many of the women perceive when they are turned on. The vagina changes color, turning purple-pink.
The clitoral hood swells, and the clitoris itself lengthens. Remember that the swollen hood, in many women, does not show the clitoris even if it has been lengthened. The labia majora are separated and raised. The labia minora swell and expand. Your heart rate progressively increases and your blood pressure rises .
Orgasm phase
At the moment of approaching orgasm , the redness increases in relation to the intensity of the arousal.

As soon as orgasm begins, the woman suffers a loss of voluntary muscle control. Contractions and spasms appear in muscles throughout the body, and especially in the genital area. The rectal sphincter also contracts, with involuntary jerks.
The respiratory rate increases up to 40 inspirations per minute, twice the normal at rest. The heart rate increases up to 180 beats / minute. Coinciding with orgasm, there are a few contractions of the orgasmic platform, 5 to 12 times, as well as the uterus . The end of these contractions marks the end of orgasm. consequences..
