It is an acute purulent inflammatory process caused by pyogenic microorganisms associated with the susceptibility of the individual, located in the soft wall of the periodontal pocket. It is the most frequent complication of periodontal diseases.
Pathogeny
1. Occurs in the presence of a periodontal pocket, when pyogenic microorganisms penetrate the connective tissue, the soft wall associated with other factors that condition individual susceptibility.
2. Deep tortuous pocket, always with the existence of pyogenic microorganisms.
3. Introduction of bacteria into the bag wall during subgingival scaling and probing.
4. Lateral root perforation during a TPR or false pathways; longitudinal fracture of teeth.
5. Periapical abscesses associated with pulp infection can drain along the root and appear as periodontal abscesses. Unquestionably, there are a large number of periodontal abscesses that have a combined apical periodontal origin that extends near the apex of the teeth, with accessory pulp canals in which case the pulp can be affected by periodontal injury and in turn a pulp infection can lead to periapical abscesses, with periodontal drainage.
6. Orthodontic movement of a tooth against the existing infraosseous periodontal pocket.
7. Placement of a crown or bridge on a molar with compromised furcation.
Clinical features
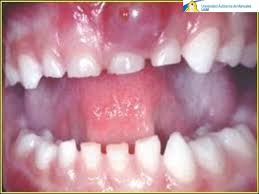
The gingiva appears as a rounded or ovoid elevation with an edematous appearance, corresponding to the lateral surface of the root. The shape and consistency vary, in some cases they are dome-shaped and relatively firm, in other cases their shape is pointed and the consistency is soft. Generally, gentle digital pressure on the lesion causes pus to escape through the lumen of the bursa. This abscess is usually accompanied by pain on palpation, and on percussion, pulsating, radiating, and tooth mobility. It may be accompanied by general malaise, fever, leukocytosis, and enlarged lymph nodes.
Histopathological characteristics
Like the gingival abscess, it consists of a purulent collection surrounded by a diffuse infiltration of polymorphonuclear leukocytes, edema and vascular engorgement.
Radiographic Characteristics
Its radiographic image is described as that of a localized area of radiolucency related to the lateral face of the root; however, it must be taken into account that on the free faces its presence is masked by the radiopacity of the root, interproximal lesions are from the radiographic point of view, those that are best observed.
Diagnosis and Prognosis
Diagnosis is based primarily on clinical findings, although in certain cases radiography can be helpful. The prognosis is favorable depending on the disease that previously exists.
Differential Diagnosis
It should be done between the periodontal, gingival and periapical abscess.
Treatment
They are seen urgently and are consulted to define the continuity of treatment once the acute phase is controlled. It consists of draining the abscess for which the following steps are followed:
1. Anesthesia by conventional methods or with natural and traditional medicine (acupuncture, homeopathy and hypnosis).
2. Vertical incision in the area of greatest decline, sometimes the incision is not necessary, and the drainage is done through the bag.
3. The dental cement is scraped, removing all the present tartar, and the soft wall is curetted.
4. The area is washed with saline solution or 0.2% aqueous chlorhexidine and gauze dressings are placed.
5. The patient is instructed to mouthwash with warm saline, analgesics, and dentogingival brushing.
6. Phytotherapy : After draining the abscess, indicate mouthwashes with Calendula , Greater Plantain or Chamomile 3 times a day.
7. Propolis : After the drainage of a periodontal abscess, wash with 5% propolis tincture.
8. Homeopathy: According to the individuality of each patient, the following medications can be indicated: Hepar sulfur, Silicea, Lachesis, Pyrogenium, Tarentula cubensis, Myristica sebifera, Antharacinum.
9. If there are systemic manifestations (fever, lymphadenopathy, among others) the indication of Antibiotics is valued .
10. It evolves after 48 hours.
