It is the accumulation of pus that arises from an abnormal communication that exists between the anal canal and the skin around the anus , which is called a perianal fistula. The anus is the terminal orifice of the digestive tract through which stool exits in the process of defecation .
It is located in the lower pole of the perineum and is the final part of the anal canal, with a duct about two centimeters long. The anus consists of two sphincters that control stool retention or output, the internal anal sphincter, which is involuntary, and the external, muscular, which is voluntary.
The anus is covered by thinner skin than usual, lacking both glands and hairs . Inside the anal canal there are glands that flow into structures called anal crypts . If these glands become blocked and they become infected, accumulating pus in them, what is known as a perianal abscess occurs.
Symptoms
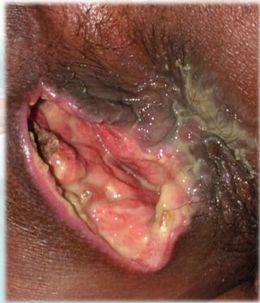
The main symptom of a perianal abscess is the pain it produces. It is an initially dull pain , rather a discomfort, which becomes more intense as the abscess increases in size. The patient will notice a lump in this area, generally lateralized, a reddish lump, hot, with tight skin and painful to the touch.
As it is an infection, there may be symptoms and signs of systemic infection, such as high fever , chills, general malaise, fatigue, muscle and osteoarticular pain. Bowel movements are usually painful and due to inflammation a certain degree of constipation may occur.
A complication of abscess is that a fistula occurs, that is, that a conduit is created through the different layers of the anal canal, making its way to the skin to drain its purulent content. Perianal abscesses are classified according to their anatomical location .
The diagnosis is simple and is based on the verification of symptoms and signs such as fever, mass, flushing, emission of pus , etc. The presence of a reddish and hot inflammatory mass on the margin of the anus is practically diagnostic of this pathology. Take a sample of the abscess material to perform a microbiological culture and determine the causative germ . Guide more specific antibiotic treatment . For the diagnosis of abscesses located deeper within the anal canal, an endoscopic ultrasound is performed , since the clinical manifestations are not so evident.
Diagnosis
The diagnosis will be based on the symptoms, on the symptoms explained by the patient and on the observation and exploration of the abscess in the perianal region. Perform a rectal examination to rule out the presence of masses inside the anal canal or rectum. Imaging tests are not usually necessary, but if the abscesses are very deep, an anoscopy or transrectal ultrasound is sometimes performed . Nonspecific signs of inflammation can be observed on blood tests , as well as occasionally an elevation of leukocytes at the expense of the percentage of neutrophils .
Treatment
Some perianal abscesses drain spontaneously, but if this is not done, the only possible treatment is to cut them open, open them surgically to allow the pus to escape, under local anesthesia if it is not very deep or large, it is necessary to perform the drainage in the operating room with anesthesia regional, applying broad spectrum antibiotic coverage.
It is advisable to take a sample of the pus from the abscess to make a culture of it and see which germ is responsible for the infection, if when making the diagnosis the abscess is very incipient and is not consolidated, there is a risk of opening it and not drain completely, is to start antibiotic treatment and drain the abscess after a few days .
When the abscess is opened, a drain is left inside so that it does not close immediately and it is certain that the residual pus comes out, after the drainage, cures should be performed. If there is a fistula, the surgical treatment is more complex, since the fistulous tract must be located and removed, taking care not to damage the surrounding musculature.
Abscesses usually respond well to antibiotic and surgical treatment and do not leave sequelae, but depending on the location and size they can cause residual scars that compromise defecation to a greater or lesser degree.
Precautionary measures
- Preventive measures for anal abscesses consist of maintaining a good diet that does not promote constipation, maintaining proper hygiene in the anal area daily and using condoms during anal penetration.
- It is produced by an obstruction of the anal crypts that, when superinfected and accumulate pus, give rise to the Abscess.
- If it does not drain spontaneously, it must be opened surgically to allow the pus to escape.
- Follow an anti-constipation diet, maintain correct daily anal hygiene and use a condom during penetration
