It is a purulent inflammation located in the gum , which can occur both in healthy individuals and those affected by periodontal disease .
Pathogeny
It is due to the action of pyogenic microorganisms that have penetrated and established within the gingival tissues through a break in their surface. This loss of continuity of the tissue associated with the susceptibility of the individual and Microorganisms are what develop the disease .
Characteristics
Clinics
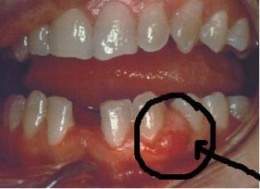
It is of rapid appearance, it appears as an increase in volume located in the papilla or the marginal gingiva, round or ovoid in shape with a taut and smooth surface and a bright red color . The injury is painful and neighboring teeth may be sensitive to percussion. If not treated, the lesion becomes fluctuating and pointed between 24 and 48 hours, and a hole may appear on the surface where the purulent exudate drains. Systemic alterations generally do not occur.
Histopathological
It consists of a purulent collection in the connective tissue surrounded by a dense infiltration of polymorphonuclear cells and edema due to vascular engorgement. In the superficial epithelium, varying degrees of intracellular and extracellular edema , invasion of leukocytes and ulceration are observed .
Diagnosis and prognosis
The diagnosis is given by the clinical characteristics of the lesion and the history of the disease that may show a history of gingival injury. Its prognosis is favorable since if the lesion is not treated it drains spontaneously.
Treatment
Steps to Drain the Abscess
1. Infiltration anesthesia, using conventional methods or with natural and traditional medicine ( acupuncture , homeopathy and hypnosis).
2. Vertical incision in the area of greater decline.
3. The incision is gently widened to facilitate drainage and careful curettage of the area.
4. Wash internally with saline solution, 5% propolis tincture, or 0.2% aqueous chlorhexidine and cover with a swab.
5. You are guided by brushing after every meal and before going to bed. Mouthwashes with warm saline solution (two tablespoons of salt in 1 liter of boiled water ) may be indicated 3 times a day.
6. Phytotherapy: Mouthwash with calendula , plantain major or chamomile 3 times a day.
7. Propolis: After draining the abscess washed with 5% propolis tincture, dissolving it in distilled water.
8. Generally does not require drainage placement.
9. Must be attended by the general stomatologist at the primary level of care.
