Tuberculosis, also called pulmonary physical disease, is an infectious disease caused by bacteria .
The bacillus’ scientific name is Mycobacterium tuberculosis , also called Koch’s Bacillus (BK).
It receives this name because it was discovered by the German doctor and bacteriologist Heinrich Hermann Robert Koch, in 1882.
The main characteristic of tuberculosis is the involvement of one of Organs most important organs of the respiratory system: the lung. Coughing attacks can be accompanied by pus and blood.
In addition to the lung, tuberculosis can affect other organs (larynx, intestines, kidneys, skin, etc.), bones, joints and tissues of the human body, being a very serious disease. If left untreated, it can lead to death.
This disease is very old and even before the Christian Era it affected several people. Previously, it was called “gray plague”.
Only in the nineteenth and twentieth centuries, due to the number of infected, did the disease gain international attention. It is worth remembering that it is considered one of the most serious and deadly diseases in the world.
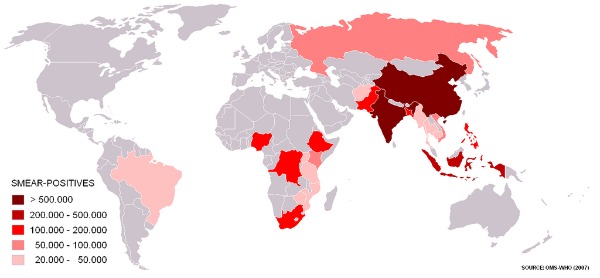
Tuberculosis in Brazil
In Brazil, tuberculosis cases are still evident, which makes it a serious public health problem, although it has decreased in recent years due to vaccination campaigns. According to the Ministry of Health (2014):
“ In Brazil, tuberculosis is a serious public health problem, with deep social roots. Each year, approximately 70,000 new cases are reported and 4,600 deaths from the disease occur. Brazil ranks 17th among the 22 countries responsible for 80% of the total number of tuberculosis cases in the world.
In the last 17 years, tuberculosis has dropped by 38.7% in the incidence rate and 33.6% in the mortality rate . ”
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of the disease is made through an exam called bacilloscopy . In addition, a chest x-ray can identify tuberculosis.
Types of Tuberculosis
In addition to pulmonary tuberculosis, there are other types of tuberculosis. They are called extrapulmonary tuberculosis and affect other organs in the human body.
- Pulmonary Tuberculosis : the most common form of the disease that affects the lungs.
- Pleural tuberculosis : occurs due to the accumulation of secretion in the pulmonary pleura, that is, a membrane that surrounds the lung. It causes pain in the rib cage and shortness of breath.
- Ganglionic Tuberculosis : when the disease bacillus reaches the lymph nodes, that is, small organs that act in the defense of the organism. This type is very common in HIV-positive patients.
- Bone Tuberculosis : also called “Pott’s Disease” (Pott’s Disease) or “Vertebral Tuberculosis”, this type of tuberculosis affects the bones (especially the spine ) causing pain and inflammation.
- Cutaneous Tuberculosis : it is one of the most serious forms of the disease. It reaches the bloodstream causing damage to the skin.
Tuberculous Meningitis
When the bacteria reaches the meninges, that is, membranes that protect the central nervous system, it is called tuberculous meningitis.
Streaming
Tuberculosis is a contagious disease which is transmitted by contact with infected people.
The patient’s secretions (sneezing, saliva, coughing, etc.) expel the bacteria and, therefore, closed places with large clusters should be avoided.
In addition to humans, the disease also affects animals. Note that people who have the AIDS virus and illness like diabetes are more likely to contract the bacteria.
Symptoms
The main symptoms of tuberculosis are:
- Fever
- Chills
- Fatigue
- Pallor
- Sweating
- Hoarseness
- Lack of appetite
- Slimming
- Persistent cough with discharge
- Chest pain
- Difficulty breathing
- Muscle aches
- Malaise
Treatment
To treat tuberculosis, the person with the disease must remain at rest, eat well, drink plenty of fluids and take antibiotics. It is worth remembering that the treatment of tuberculosis is long and can last more than 6 months.
It is advisable that the infected remain isolated in the first period of treatment, avoiding the proliferation of the bacillus.
Prevention
One of the most effective ways to prevent tuberculosis is by taking the BCG vaccine (Bacillus de Calmette and Guerin) in a single dose. It is mandatory and taken during childhood.
Good nutrition, daily exercise practices and healthy habits strengthen our immune system , making our body less susceptible to the onset of the disease.
In addition, avoiding places with intense crowding can be an alternative, since it is a contagious disease.
The BCG vaccine is applied to the right arm and usually causes a scar for life. It should not be taken by people who have the HIV virus and who have symptoms
