The dengue fever is an infectious tropical diseases more known to the world. It is caused by a virus transmitted by the Aedes aegypti mosquito .
It is a serious public health problem in tropical countries, in which environmental conditions favor the proliferation of the mosquito that transmits the disease.
In Brazil, the Ministry of Health estimates that 500 cities may suffer from outbreaks of the disease in 2019.
Transmission of Dengue

The dengue virus is an arbovirus, those that are transmitted by insect bites, belonging to the genus Flavivirus and family Flaviviridae .
There are four types of dengue virus worldwide. Thus, when a person is infected with a type of serotype, he becomes immune to it.
Dengue vectors are mosquitoes of the genus Aedes , with the species Aedes aegypti responsible for the transmission of dengue in the Americas.
The transmission of dengue occurs through the bite of the female mosquito of Aedes aegypti , as long as it is infected by the virus because it previously bitten a person with the virus.
Transmission from person to person is not possible, that is, through contact with the sick person. Likewise, the virus is not transmitted through contaminated food or water.
The person may get dengue more than once in his life. However, as there are four serotypes, it becomes immune to what has already been in contact.
Dengue symptoms
Dengue has two main forms, classic dengue and hemorrhagic dengue, which differ by their symptoms. However, in many cases the patient has no symptoms.
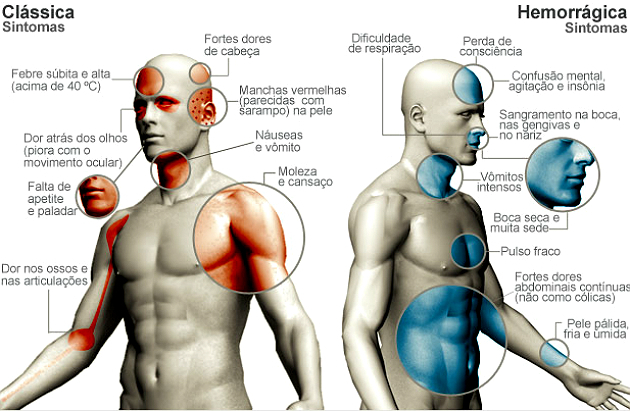
Classical Dengue
Classical dengue is the most common and mild form of the disease. Often its symptoms are confused with those of Zika .
The symptoms of classic dengue are usually felt for 7 to 15 days and are as follows:
- High fever (39 ° to 40 °): Suddenly onset, being the first symptom to appear;
- Muscle and joint pain;
- Weakness;
- Loss of appetite;
- Nausea and vomiting;
- Headache;
- Pain behind the eyes;
- Stains and itchy skin.
Hemorrhagic Dengue
Hemorrhagic dengue is a more serious form of the disease, at first the symptoms are similar to those of classic dengue. However, they are accompanied by other symptoms:
- High fever;
- Unexpected bleeds;
- Liver enlargement;
- Abdominal pain;
- Blood circulation problems.
Dengue Treatment
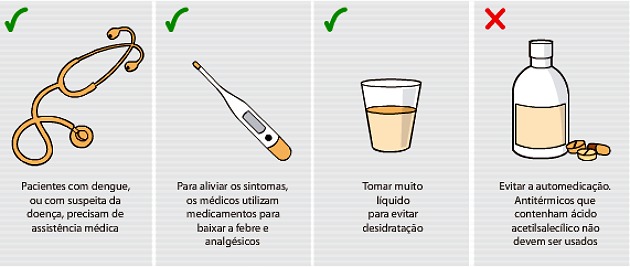
The treatment of dengue is differentiated according to its type. In general, it is recommended to rest, drink plenty of fluids and not self-medicate.
There is no specific treatment. To relieve symptoms, analgesic and antipyretic drugs (paracetamol and dipyrone) are administered.
In addition, some types of medication such as salicylates and non-hormonal anti-inflammatory drugs should be avoided.
The treatment of hemorrhagic dengue requires greater care, and the patient requires medical hospitalization.
Dengue prevention
Dengue can only be combated by eliminating Aedes aegypti mosquitoes . That is why popular participation and campaigns to combat mosquitoes must be constant, especially in areas at risk of disease transmission.
The mosquito lays its eggs in still water. Therefore, eliminating their breeding grounds is essential to reduce the proliferation of mosquitoes.
Check out some tips to avoid dengue:
- Avoid the accumulation of water in backyards, either in containers or on the next soil;
- Keep the water tanks closed;
- Check that there is no water accumulated in old tires;
- Clean water containers for pets;
- Use protective screens on windows and doors;
- Putting sand in plant pots;
- Avoid the accumulation of garbage;
- Clean the gutters of the houses;
- Use repellents in hazardous areas.
