A very common condition in people, and consists of inflammation of the shoulder with great pain that makes movement of the arm difficult. (Shoulder Bursitis, Tendinitis)
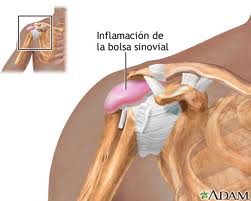
Shoulder Bursitis
The syndrome of inflammation of the shoulder (impairment syndrome) is due to a problem or a combination of problems, including inflammation of the lubricating bag or bursa (synovium) located just above the rotator cuff, this is called bursitis; inflammation of the rotator cuff tendons called tendonitis; and calcification of tendons due to wear, injury, or tears. Rotator cuff tear is a possible result of shoulder inflammation.
Stopping your advance
Bursitis:
When the arm is extended frequently, at high speed and with great load (for example when throwing the ball in baseball), this can cause bursitis. There are other non-sports activities that can cause bursitis, such as painting walls, wallpapering walls, putting up curtains, and washing windows. Medical research has shown that bursitis is more likely to develop as we age.
Tendonitis:
Tendonitis develops over a period of time and is generally seen in those whose muscles are not in good condition and decide to start a rigorous physical training program. In young athletes the elements that cause tendinitis are similar to those that cause bursitis.
Signs or symptoms
Patients generally try to ignore the symptoms of shoulder problems. There is no specific time when a person feels that there is a problem with the shoulder, at first they may feel a little pain or a slight loss of strength and do not pay attention to the loss of mobility, especially the ability to raise the arm. above the head.
Bursitis:
Symptoms of shoulder bursitis include sharp pain and limited movement.
Tendinitis :
The inability to hold the arm in a certain position indicates the existence of tendonitis. If the problem is recurring, it may indicate a rotator cuff tear.
Initial treatment
Bursitis :
Once bursitis is diagnosed, the recommended treatment is rest. If necessary, an ice pack, anti-inflammatory medication, steroid injections, and ultrasound therapy may be recommended. Some patients even need to use a sling. The patient will need to perform exercises that strengthen the shoulder once the inflammation has disappeared.
Tendinitis:
Acute tendonitis usually goes away if you avoid doing the activity that caused the tenditis and give your shoulder enough time to rest. Later, the patient can resume activities if you apply mild heat, if you do stretching exercises before starting the activity and if you apply ice packs at the end of the activities. In the most acute cases, it may be necessary to take anti-inflammatory medications or give cortisone injections.
Next step if initial treatment is unsuccessful
Bursitis:
In cases of acute bursitis, a surgical solution may be necessary.
Tendonitis:
Before recommending surgery, your doctor may recommend additional tests to determine that there is no other medical condition.
Prevention of further damage
Attention must be paid to injuries caused by excessive use. However, in many cases, patients do not go to the doctor when there is inflammation and they think they can work and bear the pain, “which will pass.”
Don’t try to “relax” tension by playing tennis or golf. If you don’t pay attention to your shoulder injury, it can become a chronic problem.
If you feel pain in your shoulder after a lot of physical activity, especially if you have reached the limit of your endurance, rest. If the pain continues or worsens, see your orthopedic doctor.
