The bupivacaine known as anesthesia, strictly medical application for prolonged duration and powerful radio application procedures used in post-operative cancer to relieve pain; In injection it is used through intramuscular, epidural, intra-articular, even perineural dosing. Bupivacaine is four times more potent than lidocaine; its action begins with more delay, but lasts about 6 hours. It is available in bottles with concentrations of 0.25% and 0.5% with or without epinephrine. There are also 1.8 ml vials in concentrations of 0.5% with epinephrine 1: 200,000.
Bupivacaine, as a powerful analgesic, is a drug that is used locally or traditionally (intravenously) by anesthesiologists, to numb their patients and thus be able to make important incisions in the body in long-term surgeries. This same medicine blocks the impulses that the nervous system sends to the body, where these in turn are the ones that send the signals or stimuli of pain or pleasure to the brain. In this sense, it is also applied as local anesthesia to perform infiltrations, as a regional analgesic to paralyze the peripheral and central nervous system. It is used in surgeries such as surgical anesthesia or analgesia, it is even used in obstetrics, that is, epidural, spinal anesthesia.
Pharmacokinetics
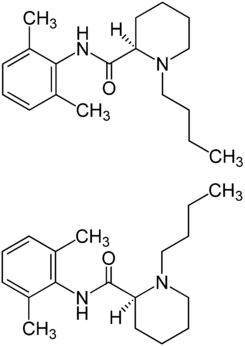
These high concentrations of bupivacaine are distributed through the bloodstream and in a high way reaches the heart, brain, liver and even the lung. Once this substance is absorbed by the tissues and is in the liver, it is eliminated through the urine where only 5% of the delivered dose will be excreted. Bupivacaine is composed of: • 2-piperidine carboxamide • 1-butyl-N- (2,6-dimethylphenyl) – • monohydrochloride • monohydrate
It has the following structural formula
Therapeutic indications
- – 0.25% and 0.5% preparations: infiltration anesthesia, conduction anesthesia, epidural anesthesia, spinal anesthesia, diagnostic and therapeutic blocks, epidural and caudal anesthesia for vaginal delivery
- – Preparations at 0.75%: epidural anesthesia in surgery and retrobulbar block.
- – 0.5% hyperbaric preparations: intrathecal anesthesia (subarachnoid, spinal) in surgery and obstetric processes. Indicated in lower abdominal surgery, gynecological (including caesarean section and normal vaginal delivery), urology and lower limbus, including hip surgery, with a duration of 1.5-3 h.
Here you can see the dosage of this anesthesia. Epidural:
- 3-5 milliliters (25 – 50 milligrams) partial motor block
- 50-100 milligram moderate motor block
- 75-100 milligram complete motor lock
Flow:
- moderate motor blockage of 37.5-75 milligrams
- 15-20 milliliters (75-150 milligrams) complete lockdown
- peripheral nerve block: 5 mL (25-175 milligrams
- sympathetic block: 50 –125 milligrams
Infiltration:
- up to 175 milligrams. Dosage can be repeated every few hours, as needed.
Mechanism of action
From the beginning of its application, bupivacaine has a moderately slow mechanism of action, that is, between 10 to 20 minutes.
Side effects
Overdose of this pain reliever can produce severe consequences or what are known as side effects:
- Acceleration of the heart rate.
- It generates anxiety.
- It generates a blurry vision in the person to whom it was given.
- In extreme cases cardiac arrest.
- Nervous collapse.
- The person becomes more prone to chills.
- The person to whom it was given has moments of confusion / disorientation.
- The person may have seizures.
- Prolonged dizziness
- Pupil dilation.
- The person has unusually high body temperatures.
- Headache.
- High blood pressure, in cases where the doses are given are epinephrine.
- Heart function deteriorates rapidly.
- Loss of consciousness for long periods of time.
- The person feels a metallic taste in their mouth.
- Extreme asthma attacks occur.
- It is known from tingling, this due to the numbing effect that this pain reliever has.
- Ringing in the ears.
- Serious allergic reaction, this can be fatal.
- Deeper breathing.
- In extreme cases, respiratory arrest occurs.
- Swelling in case of being allergic
- Exaggerated tremors.
- The person excretes less or nothing.
- Vomiting
- Weak pulse
Contraindications
- People with hypersensitivity to drugs.
- In obstetric anesthesia in the first trimester of pregnancy, and women during lactation.
- People with neurological pathologies.
- Spinal cord malformations, sepsis, severe hypertension, poliomyelitis, pernicious anemia. paralysis, chronic back pain or in individuals whose anatomy may suffer from persistent paresthesias. Infants and adolescents under 16 years of age and the elderly are more prone to the toxic effects of bupivacaine.
- Contraindicated in case of infection or inflammation of the injection site, bacteremia, platelet abnormalities, thrombocytopenia, increased bleeding time, uncontrolled coagulopathies or anticoagulant treatment.
- Patients treated with bupivacaine to achieve retrobulbar ganglion block
Dose
In principle, the dose will depend on the person to whom it is applied, be it an adult or a child, depending on size and weight, blood flow, the desired duration and if they have a medical condition; also if the drug is mixed with other competent, and especially the type of operation to be carried out
Action time
It is an anesthesia that lasts approximately half an hour (30 minutes), so the Surgeon is obliged to proceed with the operation immediately and must avoid any kind of delay.
- Adult dosage:
Infiltration: 0.25% locally infiltrated: 175 mg maximum
- Pediatric dosage:
Children under 12 years: not recommended. Children older than 12 years: 0.25% locally infiltrated: 175 mg maximum
