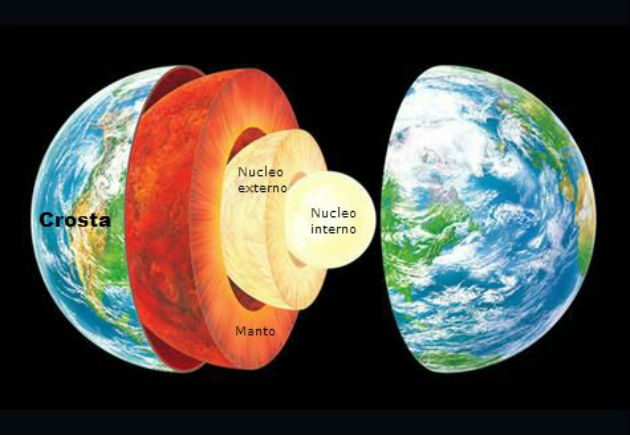
The Earth is made up of three layers, the crust, the mantle and the core. Each layer has different characteristics and temperatures, becoming warmer as it approaches the core.
Man has never reached the Earth’s core, but the study of the planet’s internal structure is possible thanks to the studies of geophysicists, who are dedicated to the study of seismology. They observe the phenomena of seismic waves and rely on devices to define the characteristics of each layer.
Which layers of the Earth?
The Earth is formed by three layers:
- Terrestrial crust : more superficial layer, of relatively thin structure and quite rocky.
- Mantle : located below the crust, it has solid properties.
- Core : Earth’s innermost, warmest layer. Features two portions:
- External core : formed by nickel and liquid iron.
- Inner core : also formed of nickel, but with solid iron.
Earth’s crust
The Earth ‘s crust is the outermost part of the Earth, which involves the entire planet and where we live. This layer is formed by rocks rich in silicon, magnesium and aluminum.
This layer is 0 to 40 km thick, varying between continents and oceans.
The crust is formed by large solid portions called tectonic plates, which move slowly over the Earth’s mantle.
The region called Mohorovicic Discontinuity, divides the crust of the Earth’s mantle.
Cloak
The mantle is the most extensive layer, located below the Earth’s crust. It is formed by different types of rocks, such as silicon and magnesium, which remain in a liquid state as a result of the heat emanating from the core.
The mantle is divided into two layers: upper mantle and lower mantle. The lower mantle remains at high temperatures, reaching up to 2,000 º C. It can reach up to 3 thousand kilometers in depth from the lithosphere.
The lithosphere , formed by the earth’s crust and upper mantle, is at least 70 km thick just below the continents and almost 10 km below the ocean.
It is divided into large portions called tectonic plates that move slowly over the Earth’s mantle.
The lithosphere rocks are divided into magmatic or igneous rocks, formed by the magma that solidifies; sedimentary rocks , formed by erosions and metamorphic rocks , which are formed by magmatic and sedimentary rocks .
Gutenberg’s Discontinuity divides the mantle and core regions.
Core
The nucleus corresponds to almost a third of the entire land mass. It is mainly composed of the metals iron and nickel. Therefore, the nucleus can also be called nife, due to the presence of these two chemical elements.
This layer is divided into an inner and outer core. The temperature of the outer core is between 2,900 and 5,100 km, it is more fluid and its temperatures vary between 3,000º C and 3,800º C. The inner core is 5,100 to 6,370 km, being solid.
Only in 2013, scientists were able to determine the temperature in the Earth’s core, which can reach 6,000 ºC, the same as the Sun.
According to scientists, the temperature of the Earth’s core is so high that iron can be taken to a liquid state. The material, however, returns to the solid state as a result of pressure, which causes it to group again.