Norway is a European country located on the Scandinavian peninsula. Norwegians enjoy an excellent quality of life.
European country, located in the western part of the Scandinavian peninsula, Norway is bathed by the Atlantic Ocean and has land borders with Sweden, Finland and Russia. Part of the national territory is located to the north of the Arctic Circle, a place where the Sun remains visible for 24 hours in summer, hence the origin of the term “Land of the Midnight Sun”.
Norway has an extensive coastline, cut by fjords (narrow and deep gulfs, bordered by mountains). These physical characteristics provide beautiful landscapes, in addition to boosting fishing activity.
With an extremely prosperous economy, the country is a major producer of oil (responsible for 50% of exports) and natural gas. Fishing is another activity of extreme importance for the national economy, especially cod, anchovies and tuna. Industries are concentrated in the capital, Oslo, and in cities like Bergen and Trondheim.
Norwegians enjoy an excellent quality of life. According to a report released in 2010 by the United Nations (UN), that nation has the highest Human Development Index (HDI) in the world: 0.938. Environmental sanitation services serve all residences; the infant mortality rate is one of the lowest: 3 deaths per thousand live births; all inhabitants over 15 are literate.
Flag of Norway
The flags of the different countries are important identity elements for the affirmation of information that these countries consider representative of their configuration or their historical past.
Often, symbolisms that refer to events of importance in the history of countries, such as wars, emancipation, the heroes who fought for the country, are represented on the flags. On other occasions, the cultural or even economic aspects of those territories are highlighted, emphasizing, for example, natural wealth.
The flag of Norway , besides presenting a very interesting graphic aspect, also has an interesting curiosity, because from it, you can design several other country flags, using pieces of its configuration.
Meaning of the flag of Norway
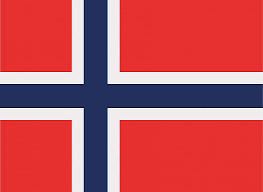
The flag of Norway is configured from a predominantly red background, on which is laid a Nordic cross , or Scandinavian cross, in white tone on the outside of the design and blue on the central part of it.
The cross is not exactly centered, but occupies the left portion of the flag more, ending at the four ends of the flag. In this official flag there are no other graphic symbols or colors, only the Scandinavian cross represented, which begins and extends from the hoist, part of the flag where it is attached to the mast.
The symbolic element of the Norwegian flag, the so-called Nordic cross, is also used by other Scandinavian countries, with all Nordic countries using this symbol pattern.
Norway climate
Norway’s climate is worthy of a legitimate Mammoth! Winter is harsh, with intense cold for much of the year. The low temperatures, however, do not scare the Norwegians, who live well with the climate, whether it has rain and snow or not.
According to Visit Norway , Norway’s average winter temperature is -6.8 ° C. The lower continental regions, in addition to northern Norway, have the harshest climate, with very cold, wind and snow. The fjords and southern Norway, on the other hand, have milder temperatures, but it is worth remembering that for the local climate. For us Brazilians, used to the tropical climate, it remains very cold!
Recalling that the Nordic countries are those that form a region of Northern Europe, as well as the North Atlantic, represented by Denmark, Finland, Iceland, Norway and Sweden , as well as the autonomous regions of the Faroe Islands, the Aland archipelago and Greenland.
Nordic cross
The Nordic, or Scandinavian, cross represents Christianity , being that the first flag that presented this graphic resource was the one of Denmark, being adopted later by several other countries. Fredrik Meltzer, a leading Norwegian executive, considered that Norway should also have the cross on its flag, as well as other countries in Scandinavia.
Likewise, the colors are practically standardized among the Nordic countries, creating an identity in the region from the configuration of the flags, all bearing the Nordic cross in their compositions.
Merchant Navy Flag
Norway also presented other officially used flags, such as the Merchant Navy Flag, which was used during the period of union with Sweden, between the years 1814 and 1899.
Since the red background, with the Nordic cross overlapping, were present, however, a union of colors was made in an emblem placed in the upper left corner of the flag, which became known as “Sildesalaten”. This flag was widely used in Norway, which defined the union between it and Sweden.
However, with the weakening of this union, the use of the emblem was withdrawn still in 1899, leaving the background configuration of the flag as it is known today. With the dissolution of the union, in 1905 this symbol was also removed from the flag of the Merchant Navy, and Sweden kept it until this same year in all its flags.
Colors
Regarding the colors used in the flag, there is a proposition that states that these are based on the colors of the flags of countries like France and the United States, which were considered as symbols of free countries in the early 19th century. Thus, white and blue colors theoretically represented freedom and democracy .
There is also an idea that the colors were chosen as a way of creating a sense of identity among the Nordic countries, so that the red and white colors used would be a reference to the Danish flag, while the blue used is a reference to the Swedish flag.
Despite the assumptions, the truth is that there is a pattern among the countries of Scandinavia regarding the colors officially accepted in their flags, creating a sense of identity region among them. There is also a curiosity about the flag of Norway, which can be used as a basis for clipping the flag of several other countries, such as France, Finland, Poland, Thailand, among many others.
Norway: characteristics and curiosities
Norway, officially called the Kingdom of Norway, is one of the Nordic countries in Northern Europe . Norway has a land area of 385,203 km², and its geographical boundaries are the Norwegian Sea and the North Sea in the West, Sweden in the East, Finland and Russia in the North and Skagerrak Sea in the South.
Physical characteristics
The physical characteristics of the country range from high plateaus and mountains in much of the territory, as well as the presence of fertile valleys. One of the most prominent elements in the physical configuration of Norway are the famous fjords , located in the coastal regions, which attract many tourists.
Happiest country
Norway has a high Human Development Index (HDI), prevailing for several years at the top of the list of best countries to live in. In addition, Norway received the designation of “ happiest country ” in 2017, conferred by the World Happiness Report.
economy
In addition, Norway has a high per capita income (calculation that takes into account the gross national product, subtracting capital depreciation expenses and indirect taxes), as well as a very high life expectancy of the population, reaching over 81 years . In 2016, the population of Norway had more than 5.233 million inhabitants.
Highlights in the economy of Norway are oil and industries, with highlights in the country’s export sector, oil and its derivatives, as well as metals, machinery and equipment and fish, with Norwegian fish being one of the most appreciated and expensive. of the world.
The Norwegian industry stands out for the production of processed foods, still for cellulose and chemical products, as well as in the area of shipbuilding.
The countries to which Norway exports its production are mainly the United Kingdom, the Netherlands, Germany and Sweden. The imports in Norway come mainly from Sweden, Germany, China and Denmark.
Curiosities
There, during autumn and winter (that is, half of the year), the sun barely appears and, in some places, there is a total lack of sunlight. This is the case of the village Rjukan, located in the middle of a valley. There, the exit found was to place mirrors seven meters high in the highest part of the place, so that the equipment reflected the sunlight into the small Norwegian village.
Language
The official language is Norwegian, but most of the population also speaks English fluently.
