The Australia , considered country-continent, is the sixth country in area, with a total area of over 7.7 million square kilometers. Its area is surpassed only by Russia, Canada, China, the United States and Brazil.
This country of extensive coastline is bathed by the Indian and Pacific oceans. Among the few islands off its long coastline, the island of Tasmania stands out, separated from Australia by the Bass Strait, in the southeast of the country.
The territory is divided into six states : Queensland, New South Wales, Victoria, Western Australia, South Australia and Tasmania, in addition to two territories, the Northern Territory and the Australian Capital Territory (Canberra).
Australia flag
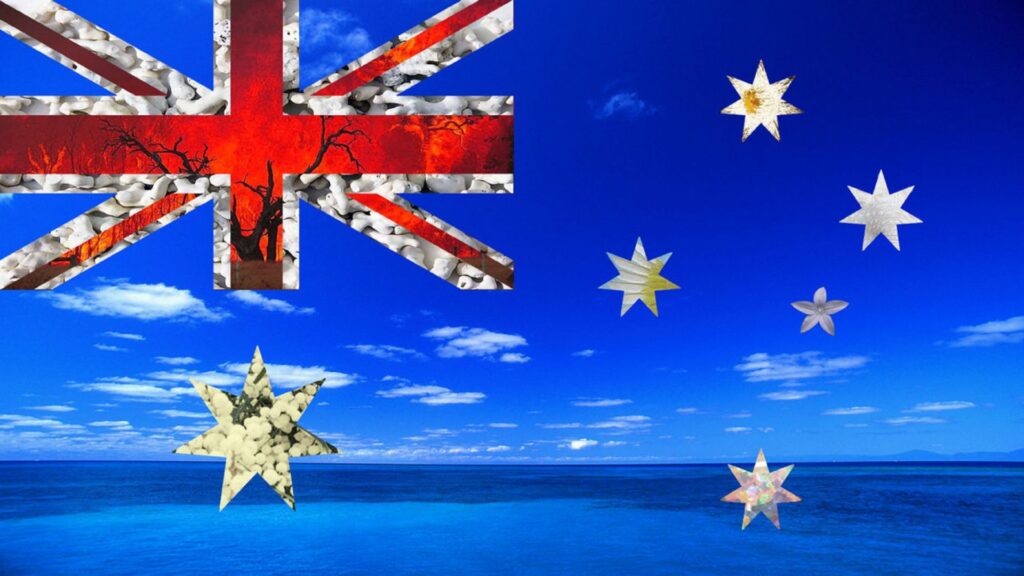

The flag of Australia has been the official national flag of the country since 22 May 1909.
The Australian flag is based on the blue Ensign, and can be divided into three elements:
– The upper left canton has Union Jack, the flag of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, as a sign of the this country’s influence to Australia and belonging to its community.
– Links, under Union Jack, a great white, siebenstrahliger Stern, the Commonwealth star is called the will. Six rays represent the six states of Australia, the seventh for the territories.
– The right half is an arrangement of five other white, stars of different sizes, representing the constellation of Cruzeiro do Sul. One is fünfstrahlig, the remaining four siebenstrahlig.
Australian flag history
The first recorded attempt to introduce a “national flag” to Australia, dates from 1822 to 1823, and returns to the two captains John Nicholson and Bingle John. The flag, known as the Colonial National Flag, consisted of a white cloth with the red cross of São Jorge, which at each end was wearing a white star, which must be available for the Southern Cross. Some time later, a fifth star was also included, to represent the colonies of Australia. Bingle was outraged and wrote in his 1881 memoirs:
“The person who added one more star to another colony was” American thinking in motion “and did not understand the original intention, which was simply the emblem of our hemisphere, Southern Cross.
The proper appearance of the Colonial National Flag is controversial. Exam are versions that are based on Ensign Branco (Cruz de São Jorge with Union Jack in the upper canton) and have a star with five or eight points. It is indisputable that from this point, the star, symbol of the Southern Cross, the symbolism of another Australian flag dominated. In 1831, Captain John Nicholson beat New South Wales before a flag at sea, the New South Wales Ensign. This flag has become increasingly popular in Australia and has gained importance as a federal symbol. The Federation movement, had with groups like the Australian Native Association and the Australian Federation League in 1880 and 1890, its origin, and set up this flag. The league motto said was:
“One people, one destiny, one flag”
The New South Wales Ensign is also referred to as the Australian Federation Flag or Australian Ensign and is for many the first Australian royal flag also represents these exist numerous similar versions with four, five or six stars, which in turn 5-8 points passed.
Meanwhile, star symbolism has been done on many other flags in Australian history. In 1851 he formed the Anti Transport League, fought against Zutransport another of those condemned to Australia and New Zealand. The five golden stars of Cruzeiro do Sul were at the same time for colonial settlements in Tasmania, Victoria, New South Wales, South Australia and New Zealand. On the white margin was the name and year of the foundation of the league, and the name of the colony. The flag of the Anti Transport League was very similar to the national flag today and its influence can be seen in the current flag of Victoria.
Another important flag in the flag of Australia’s history was known as the Stockade Eureka flag. She blew the Stockade Eureka 1854, the camp of some prospectors in Ballarat. These miners, united under the leadership of Pedro Lalors, sat down for the release of captive compatriots, universal suffrage, secret ballot, and many other reforms. His flag only flew from November 3 to December 3, before the police violently broke the camp. This blue and white flag with stars is now at the Eureka Museum Stockade Center in Ballarat.
On 1 January 1901, the day of the founding of the Commonwealth of Australia, the country still had no official flag. Australians therefore investigated by creating a new flag for an identity without denying loyalty to the British crown. In 1900, he called the Evening Herald and then in October, commented on Australasian Comments, both Melbourne magazines, in a winning flag competition. On April 29, 1901 finally excluded one from the government competition, during his evaluation of the proposals were taken into account in the review of Australasia Comments. The cash prize increased the use of the government and the Havelock Tobacco Company from £ 50 to £ 200, which by that time was a significant amount. The competition still has its effect, and there were 32,823 drawings posted.It was clear from the start that it would be equivalent to a flag that includes Union Jack and Cruzeiro do Sul. Deviating flags were hardly given a chance to win. In addition to this symbolism contained many motifs drawings of the local fauna. The most unusual designs included a kangaroo jumping through the Southern Cross, cricket playing Australian animals, a sechsschwänziges kangaroo for the six Australian states and a fat kangaroo, which points a gun at the Southern Cross.a sechsschwänziges kangaroo for the six Australian states and a fat kangaroo, which points a gun at the Southern Cross.a sechsschwänziges kangaroo for the six Australian states and a fat kangaroo, which points a gun at the Southern Cross.
The shared prize Finally, five participants whose proposals are very similar, differing only in details from each other. Selected was a dark blue flag with Union Jack (Blue Ensign) with a large Commonwealth star and five smaller ones, arranged like the Southern Cross star constellation. These winning flag went like this, almost equal to the current one and differs from this only in two points: the big central star (Commonwealth Star) still consisted of six pins and the stars of Cruzeiro do Sul originally had more and more 5-9 teeth with magnitude apparent inside to take into account the constellation. This flag was the first third of September 1901 hoisted at the Royal Exhibition Building in Melbourne.
The proposed flag has never been debated in the Australian Parliament. Edmund Barton, the Prime Minister of Australia, favored the “Australian Ensign” and sent them, along with a simplified version of the competition flag for the choice of King Edward VII, on 20 January 1903 only, the government could announce the news that Edward VII approved the proposal as an official competition flag. On 2 June 1904, the Australian Parliament passed a resolution for the flag and then gave it the same status as the Union flag in the United Kingdom. There were two versions of the flag: red for merchant ships (Commonwealth red standard) and blue for other uses (Commonwealth blue standard), which led to some confusion in the flag. On February 14, 1954 Elizabeth II passed the Flags Act (CWTH, 1953).In Section 3, the Commonwealth Blue Ensign confirmed as the national flag.
The Commonwealth Star on 22 May 1909 complemented by a bite, which is for both territories. The flag of Australia, next to the flag of Jordan for just two flags that carry a seven-pointed star.
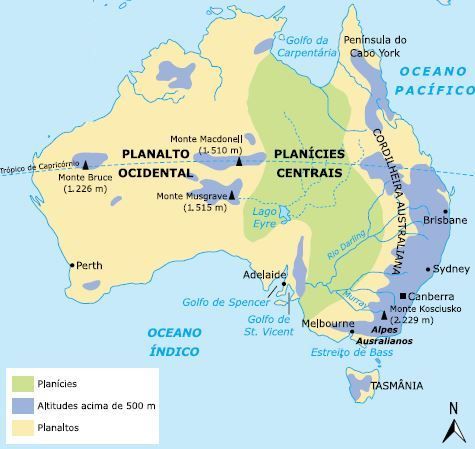
Relief
The Australian shield forms an extensive crystalline plateau, the Western Plateau , whose altitudes vary between 300 and 600 meters, and has important mineral deposits.
Along the Pacific coast is the Australian mountain range , which stretches from the York Peninsula to the State of Victoria, at the southern tip of the continent. In the southern portion of this mountain range, there is an ancient fold called the Australian Alps , in the State of New South Wales.
Between the Western Plateau and the Australian mountain range, the Central Plains are located .
Hydrography
The country is relatively poor in rivers, due to the arid and semi-arid climates that dominate large extensions. The most important hydrographic basin is Murray , with its great tributary, the Darling River , and is located in the south of the Central Plains.
The central-western portion of the country is rich in lakes. The rivers in this region are mostly temporary and tributary to Lake Eyre , with 9,583 km².
Climate
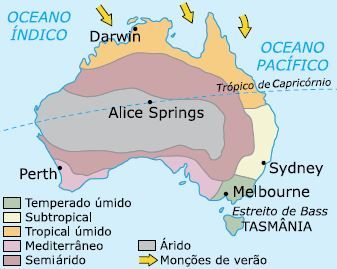
In Australia, hot and dry climates (arid and semi-arid) predominate, responsible for extensive deserts such as Vitória, Gibson and Simpson, in the Western Plateau.
In arid regions, continentality is responsible for the marked daily thermal amplitude, as occurs in Alice Springs , in the Northern Territory, where the temperature, during the day, reaches more than 47 ° C in the shade and, during the night, falls to –5 ° C.
Other types of climate in Australia are humid tropical , in the northern and eastern portions, subject to the monsoon regime; the wet temperate , of fertile land; the Mediterranean and the subtropical , with winter rains.
Vegetation

The variety of climates results in a range of plant formations in Australian territory. It includes the extensive savannas ( bush ), a consequence of hot and arid climates, and tropical and subtropical forests , with the presence of eucalyptus (tree native to Australia), which are located in the humid areas of the northern and eastern coastlines.
Fauna
Australia is known for its endemic fauna, that is, animal species that evolved in its territory and only exist there, such as the koala, the platypus, the echidna, the dingo, the kangaroo among others. This is due to its continental isolation.

Colonization of Australia
The Dutch were the first Europeans to explore Australian territory. In 1770, it was the turn of the Englishman James Cook.
In 1788, British occupation and colonization began in Australia: the English settled in the Bay of Sydney Cove, where the current city of Sydney is located. For a long time, Australia was an English agricultural penal colony.
Population
The original inhabitants of Australia were Aborigines , who were mostly exterminated by the English. These people lived off the collection, were nomads and did not practice agriculture. They were economically self-sufficient.

Colonial domination, however, has disrupted these societies, currently relegated to isolated areas of the country, the outbacks . In many communities, the native lifestyle reflects values adopted by colonizing peoples.
Initially, some factors discouraged Europeans from going to Australia: the distance between the two continents and the preference for America, relegating Oceania to the background.
The discovery of gold in Australia, in 1851, changed this situation: the country started to receive thousands of European immigrants , initially British, later Italians, Irish and Greeks (it was difficult for non-Europeans to enter the country).
Australia’s population, with 24 million people (2016 data), is concentrated in the southeast and the main cities are Sydney, Melbourne and Brisbane. Canberra, the capital, has just over 350 thousand inhabitants.
Current socioeconomic indicators – such as high HDI, low birth rates, high life expectancy and high per capita income – make Australia a modern and developed nation.
Australian Economy
It is a country that has a very diversified economy, with an industry linked from the primary sector, with the production of food, wine, tobacco and mineral exploration, to activities that require great technology, such as the machinery, equipment, products chemical, metallurgical, steel, etc.
The tertiary sector represents 71% of the country’s economy (major development of cutting-edge technology and qualified service provision), the secondary sector (industries) corresponds to 21% of production and the primary sector corresponds to 8%. In addition, some of its universities are considered research centers, such as the University of Melbourne.
Australia exports meat, wheat, wool and ores, such as bauxite, lead, nickel, manganese, gold and silver.
Australia is located between America and Asia, a strategic area of the Pacific, both from a commercial and maritime point of view, as well as from an international geopolitical point of view. International trade is carried out in a more dynamic way: today the Economic Cooperation of Asia and the Pacific ( Apec ) is responsible for a significant portion of world exports.
Australia is very well equipped to play the role of “medium power” in the Pacific Ocean.
Effect of Covid-19 on Australia’s Economy

The coronavirus pandemic has put the strongest economies on the planet to the test. Nobody escaped. Nor does Australia, which has been growing steadily for almost 30 years.
It is a unique result in the developed world. The last time the country had two consecutive quarters of fall in the Gross Domestic Product (GDP) , the definition of technical recession, was in 1991.
But over the past week, the Australian central bank has warned: “a very big” economic contraction is coming. On Wednesday, the country had its AAA rating downgraded by Standard & Poor’s from “stable” to “negative”. The risk rating agency estimates that the pandemic “caused a severe economic and fiscal shock” in the country.
The Australian unemployment rate is expected to double to 10% in the coming months, according to UBS bank expectations, similar to that of other institutions. The bank expects a 6.1% decline in GDP in 2020.
This is hard information for the place that is called ” lucky country “. The nickname was created in an ironic way in 1960, but Australia ended up earning the title due to its resilience at critical moments for the global economy, such as the 2008 crisis or the internet bubble, in the late 90s.
By 2020, however, isolation policies against the spread of coronavirus are greatly reducing activity and increasing the risk of a bankruptcy among small businesses. Bars, restaurants, cinemas and gyms have been closed since March 23.
Airlines and tourism companies also suffer from the reduced movement of people and the prohibition of non-residents from entering the country. In addition to mining, tourism is another strong sector of the Australian economy, along with education, finance and technology.
Aid calls have multiplied, and the government has announced that it will subsidize the wages of six million workers – about a quarter of the Australian population – for the next six months as a way to contain rising unemployment.
The plan is to pay 1,500 Australian dollars ($ 928) every fortnight to employees of any company that has had at least a 30% reduction in revenue. The plan is expected to account for $ 130 billion of the $ 320 billion package from the Australian government and central bank against the crisis.
Government
English is the country’s official language and, until the 1960s, Australia and the United Kingdom remained linked militarily and economically.
Australia is part of the British Commonwealth of Nations , which defines itself as a “Voluntary Association of Sovereign States”.
The country is a parliamentary monarchy, whose head of state is Queen Elizabeth II of the United Kingdom. The head of government is the prime minister.
