Chemistry is the science that studies matter, its structure, formation and the transformations it undergoes, taking into account the energy involved in the whole process.
Chemistry is part of the Natural Sciences and focuses on observing phenomena, creating theories to explain them and models that represent them.
Check out the text that Toda Matéria prepared for you to learn more about this science and its importance for humanity.
What does Chemistry study?
The matter is the chemistry study object, which in turn establishes the relationships between its formation, properties and transformations.
It is worth remembering that matter is everything that has mass and occupies a place in space. A material is made up of atoms , which group together and form the different existing chemical substances.
All the efforts to develop this science allowed the human being to know the matter and the means to transform it, so that the knowledge was used for our benefit.
Importance of Chemistry
Chemistry is present everywhere, but it is sometimes difficult to recognize. From the cultivation of wheat to bread on our table, in several stages, chemical knowledge has allowed us to improve manufacturing methods and quality of life.
Another example is that we receive materials like food, water and air in our body. Inside our organism there are several chemical transformations so that we can take advantage of nutrients, produce energy and use oxygen to stay alive.
Through Chemistry it is possible to study natural substances and take advantage of them. But also, you can produce materials in the laboratory.
Take the example of tennis, a product that contains materials, of natural or synthetic origin, that have been transformed by man to create a consumer good for society.

Simply put, we can say that sneakers are made of rubber, fabric and metal.
- Metals are ores extracted from nature.
- Rubber can be natural and produced with the sap of rubber trees. Synthetic rubber is made from petroleum.
- The natural fabric comes from cotton, while an example of synthetic fabric is nylon.
Chemistry has already been seen as a villain, due to the pollution coming from the means used to supply the market urgently and for a long time neglect the environmental issue. Toxic, non-degradable products and industrial waste dumping are some of the many problems related to chemical products.
However, this view is changing. Green Chemistry encourages cleaner production, environmental preservation and industrial processes with less waste generated. Recycling, biofuels and reduced greenhouse gas emissions are some of the measures that we can already observe in our daily lives.
What is Chemistry for?
Chemical knowledge generates applications and technologies allow new products to be created. Chemistry is present in food, medicine, clothing, construction, and so on.
Check out an example of where chemical knowledge was used.

The active ingredient in the repellent is extracted from a plant called citronella. Through laboratory equipment and extraction techniques, chemists were able to isolate citronella oil and, together with other chemical substances, transformed it into a product that prevents mosquito bites.
For that, it was necessary to study the composition of the substance, how it acts and what are its risks. This is all part of chemistry: researching, investigating, experimenting and creating products that improve people’s lives.
Although it is common to associate chemical knowledge with wars, because of the creation of chemical weapons and the atomic bomb , Chemistry has made important contributions throughout history. Some of them were:
- Alternative energy sources: discovery of the radioactivity of chemical elements and creation of nuclear energy to generate electrical energy.
- Industrialized foods: discovery of substances that preserve food and, thus, the validity of commercialized foods has increased.
- Medicines: discovery of chemical substances capable of controlling and fighting diseases.
Main areas of Chemistry
| General chemistry | Concepts and terms that are the basis for understanding the other areas. |
|---|---|
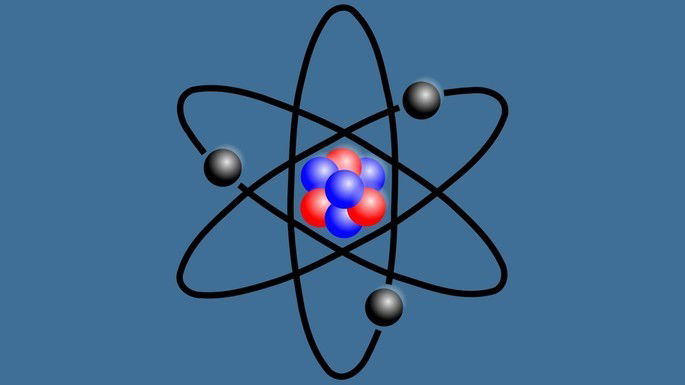 | Example:Atomic models Periodic table Matter Properties Chemical bonds |
| Physicochemical | It studies the energy and dynamics of chemical transformations. |
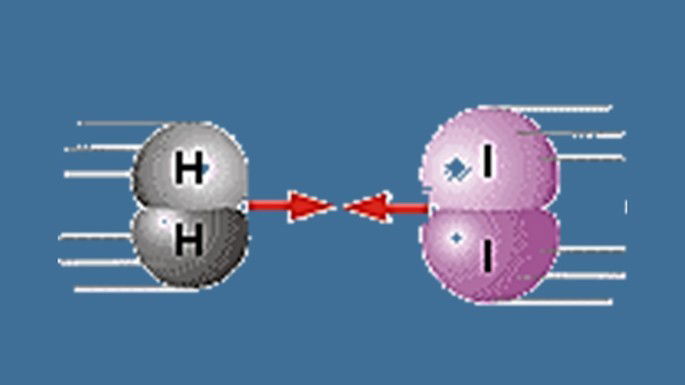 | Example:Chemical Kinetics Electrochemistry Chemical balance Thermochemistry |
| Inorganic chemistry | It studies the compounds formed by the chemical elements. |
 | Example:Inorganic Functions Acids and Bases Salts Oxides |
| Organic chemistry | It studies the compounds formed by carbon. |
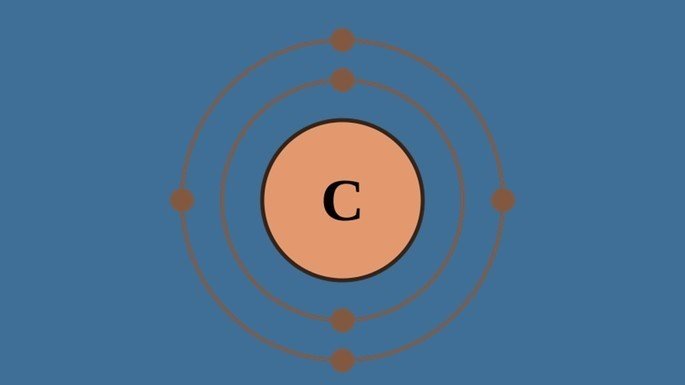 | Example:Carbon Carbon Chains Organic Functions Organic Reactions |
| Nuclear Chemistry | Study the reactions in the nuclei of atoms. |
 | Example:Radioactive elements Nuclear fission Nuclear fusion Radioactivity |
| Environmental Chemistry | It studies the chemical processes in the environment. |
 | Example:Biogeochemical Cycles Acid rain Greenhouse Effect and Global Warming Pollution |
History of Chemistry
The precursor of Chemistry is Alchemy , a practice widespread in the Middle Ages, which involved science, art and magic. For some, in Arabic, the term “Alchemy” (Al-Khemy) means “chemistry”.
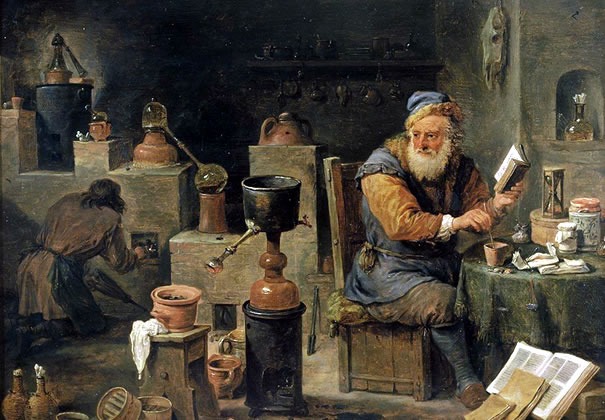

Alchemy’s goal was to create the Philosopher’s Stone, with the ability to transform common metals into gold , and produce the Elixir of Immortality, which would cure all ills and guarantee long life.
In this search, many chemical substances were created and laboratory equipment was made to carry out experiments.
The knowledge acquired by alchemists was important to support modern Chemistry, which emerged in the 18th century.
Gradually, scholars were abandoning alchemical theories and adopted experimental methods to explain the observed phenomena.
Lavoisier is considered the father of modern Chemistry for his significant contribution to the emergence of this science and consolidation of the scientific method as a new way of studying chemical processes.
