Vaporization is the change from a liquid to a gaseous state and is the reverse process of liquefaction.
A substance can undergo the vaporization process in three ways: evaporation, boiling and heating.
In the liquid state, the particles that make up the substance are closer to each other than in the gaseous state.
In this way, the bonding force between atoms and molecules is greater in the liquid than in the gas.
Thus, the substance will change to a gaseous state when there is a change in the binding force between its particles.
Evaporation
The evaporation is an evaporation method in which the state change occurs gradually.
The particles inside a liquid have variable speeds. Thus, there are particles with higher kinetic energy values than others.
These particles escape when they have sufficiently high velocity through the free surface of the liquid.
In this way, they no longer suffer the action of the internal binding forces of the liquid and go into the gaseous state.
There are some factors that influence the rate at which evaporation occurs. We can mention: temperature, nature and area of the liquid’s free surface, pressure and vapor concentration close to the liquid’s free surface.

Boiling
When a body receives heat the degree of agitation between the particles that compose it increases and consequently its temperature also increases.
Upon reaching a certain temperature value, called the boiling point , the substance will start to change its phase.
For example, water, under pressure from 1 atmosphere, begins to boil when it reaches a temperature of 100 ºC. Iron, on the other hand, will only boil when its temperature is equal to 2 800 ºC.
The boiling is a steaming process faster than the evaporation and the temperature remains constant during boiling.
In addition, for a liquid to turn completely into a gas, it must receive a certain amount of heat.
The latent heat of boiling is the amount of heat per unit mass that a body must receive to pass into the gas phase. This value depends on the substance that constitutes it.

Heating
Heating is a type of vaporization that occurs when a liquid is released on a surface that has a temperature higher than its boiling point.
In this situation, the liquid will quickly change to a gaseous state.
An example of heating is when we pour a few drops of water on a very hot plate.
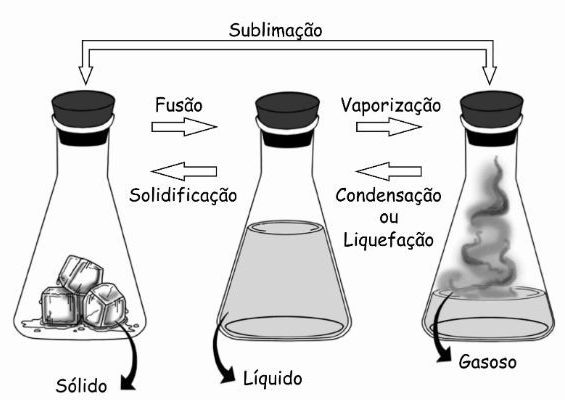
Phase Changes
In addition to vaporization there are other processes of change of state. Are they:
- Fusion
- Liquefaction
- Solidification
- Sublimation