Oxyurosis, also known as enterobiosis, enterobiasis, oxyuriasis, is a verminosis that affects the whole world and is caused by the nematode Enterobius vermiculares , from the elimination of eggs by the female. These worms can be called pinworms.
Having its origin in the African continent, it is believed that its dispersion occurred due to the migration of people between the continents.
Oxyurosis transmission
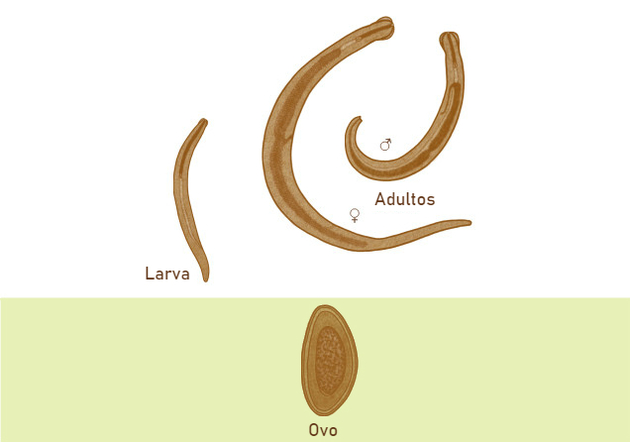
The transmission of oxyurosis usually occurs due to lack of hygiene measures and actions, being very common in children.
There are three different ways of transmitting the disease.
- Direct transmission : when the person takes the parasite from the anus to the mouth, that is, when itching in the anal area and the person takes the hand to the place and then does not wash the hands properly.
- Transmission indirectly : it is when the water or food ingested is infected, or when a person who has the worm eggs in hand greets another person. In addition, in places where basic sanitation is poor or where there is poor hygiene, eggs can be found in clothing, also increasing this form of transmission.
- Transmission by retro-infestation : it is when the larvae hatch from the anal region and migrate to the cecum, thus contributing to the cycle to restart in the person’s body.
Biological cycle of the oxyurose transmitting agent
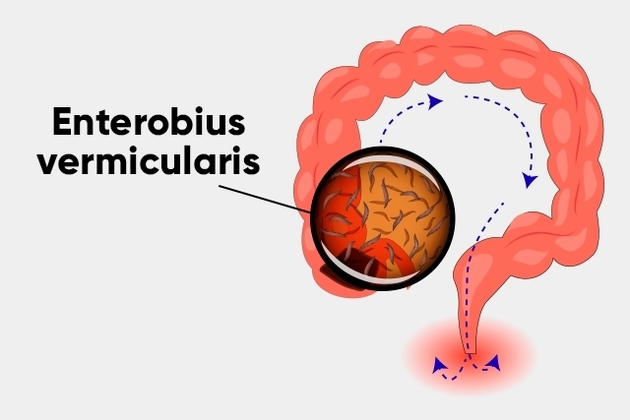
The vermicularis Enterobius has a biological cycle that begins in the person egg intake. When ingested, it goes to the small intestine .
When allocated in the organ, the larvae hatch and go to the cecum, a place used for reproduction. Larvae can be 2 to 13 millimeters in length as adults, the male being always larger than the female.
After the larvae reproduce, the male is eliminated in the feces. The females migrate to the perianal region and die shortly after laying the eggs.
The whole cycle of oxy-urns lasts approximately 40 days.
Oxyurosis symptoms
Oxyurosis can cause different symptoms that vary according to the intensity of the disease.
As it reaches the intestinal region, anal itching is the most common symptom, especially at night, as it is when the worms move between the intestine and the genital region.
Other symptoms are also common, such as:
- Stomach ache;
- Vomiting;
- Diarrhea;
- Motion sickness;
- Intestinal colic;
- Blood in the stool.
In the case of women, the appearance of vaginitis is possible due to the proximity of the vagina to the anus.
Diagnosis and treatment of oxyurosis
The diagnosis of oxyurosis is made through laboratory examination and aims to detect the presence of the female worm and possible eggs.
A collection of material is made in the anus, which is carried out the method known as gummed tape which consists of gluing a special adhesive cellophane tape.
The treatment should be done with oral intake of prescribed wormers by medical personnel as well as cleaning of the environment and personal care. In addition, in some cases the use of ointments may be indicated to enhance the reaction of the medicine in the body.
The medication may vary according to the case, and a single dose may be indicated or for a pre-defined period. In addition, it may also be necessary to repeat the treatment two weeks after the discovery of the disease.
Prevention of oxyurosis
Actions to prevent oxyurosis are related to hygiene, highlighting the following precautions:
- Have hygiene habits;
- Keep children’s nails cut;
- Wash your hands before preparing food and after using the toilet;
- In the case of infected people, boil their clothes.
