Mosses make up most of the bryophyte plants. They are small plants and of simple structure, they do not have conductive vases, flowers and seeds.
Mosses can be found in almost all parts of the world, even in frozen regions.

Features
Mosses live in humid and shady environments. They can grow under different substrates such as soil, rocks, tree trunks and even walls. Some species of mosses form true green carpets, covering large areas.
The body of the moss, called a stalk, is composed of three parts: rhizoid, cauloid and phyloid.
- The rhizoids fix the plant to the substrate and absorb water and minerals necessary for their development. Mosses do not have a true root structure.
- The cauloid consists of a small stem from which the phylloids depart.
- The phyllodes are structures responsible for photosynthesis, represent the moss leaves.
There are no specialized organs in the body of the moss to absorb water or even to transport it to more distant parts of the plant. This condition limits your growth. Therefore, mosses are always small and low.
Mosses are the first plants to emerge in the process of ecological succession , because they specialize in colonizing bare surfaces. Mosses prepare the soil for the development of other vegetables.
Moss Reproduction
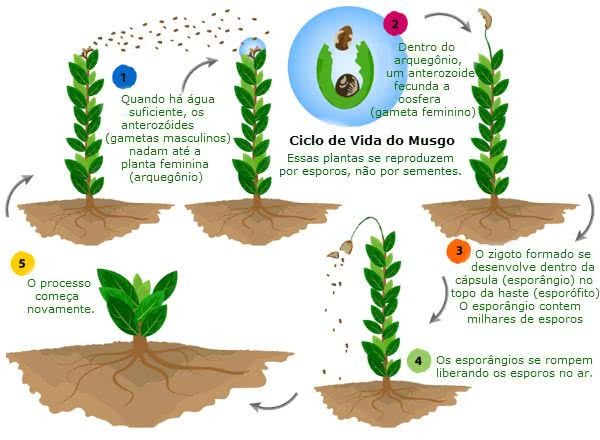
Mosses have male or female plants, they are dioecious.
Male moss produces anterozoids (male gamete) that reach the archegonium through water. Within the archegonium, an anterozoid fertilizes the oosphere (female gamete), forming a zygote (2n).
The zygote develops in an embryo. The embryo also develops and originates the sporophyte, a temporary structure of the moss, located at the end of the phylloids.
The sporophyte houses the sporangia, where the spores are produced by meiosis. When the spores are released into the environment, they restart the life cycle.
Types of Mosses
Mosses can be classified into three classes: Sphagnidae, Andreaeidae and Bryidae.
- Class Sphagnidae : “peat moss”. They differ from other mosses in that their phylloids have dead, large, perforated cells. They have great water absorption capacity.
- Class Andreaeidae : “granite mosses”. They receive this name because they inhabit mountainous regions, being found in granite rocks.
- Bryidae class : “true mosses”. It is the most diverse and abundant class.
