Christopher Columbus ( 1451 – 1506 ). Navigator and discoverer, perhaps of Genoese origin, in the service of Spain , a controversial and mysterious man, self-taught and a great observer, he arrived in what was known as the New World on October 12 , 1492 , being the first admiral, viceroy and governor of the Indies. He taught the seamen of his time the way to go to and from America.

Biographical synthesis
Early years
Christopher Columbus was born in Genoa , in a located date between August 25 and October 31 of the year 1451 , although other historians located in 1456 , with the name of Cristoforo Colombo (in Italian ) or Christophorus Columbus (in Latin ), and he was the first child of the marriage formed some five years earlier by Domenico Colombo and Susana Fontanarossa. The family had been settled in Liguria for at least a century, although its members were always peasants or artisans without means of fortune.
Domenico himself seems to have moved from Quintus to Genoa around 1429 to learn the trade of weaver. The Colombos had three other sons and a daughter, Bianchinetta. Two of these Colombo brothers were to play a preponderant and continuous role in the adventures and misadventures of the first-born: Bartolomé and Giácomo. The second of them would be called Diego in Spain.
He was barely old enough when Cristoforo helped his father in his successive jobs as cheesemaker and tavern keeper or accompanied him on business trips to Quinto or Savona. He was an alert and restless boy, but there is no evidence that he had pursued any kind of studies. What really attracted him was the port, the tales of sailors, the ships that arrived from distant lands.
Genoa was an important center of maritime trade and it did not take much for the young Colombo to enlist in ships of the great shipping companies of the city, making various commercial itineraries through the Mediterranean .
Thus he learned, in practice on deck, the trade of the sea. He spoke with the wind and current pilots, read the marine charts, and rehearsed the use of nautical instruments. At twenty he was already a good sailor.
Columbus and Portugal
In the 1470s , he arrived in Portugal where he married Felipa Muñiz and had a son named Diego. In this country he joined various Portuguese expeditions along the western coasts of Africa .
Here he also conceived the project of seeking a sea route to China and India crossing the Atlantic Ocean , believing that this was a narrow sea. In 1484 Columbus presented his project to Juan II of Portugal and asked him for financial support to put it into practice. But a board of experts deemed the plan far-fetched, and the king, more concerned with African explorations, did not want to help him. Disappointed, he moved to Castile to present his ideas to the Catholic Monarchs , since he needed the support of a monarch or a powerful nobleman to bear the expenses.
Residence in Spain
Accompanied by his son Diego, he settled in Palos de la Frontera ( Huelva ), where he came into contact with some people who helped him and who later had a prominent role in running the company. These people were the Franciscan friars of La Rabida , who put him in contact with the kings; the Pinzóns, who lent Columbus their supplies, knowledge and influences; and the Andalusian sailors, accustomed to sailing the Atlantic and who would form the crew of the Columbian voyage. The Castilian monarchs took a while to accept Columbus’s projects; It was seven years, during which frequent contacts were made with influential people at court, but the kings showed that they were more interested in the conquest of Granada .
In Spain he got the support of Queen Isabella of Castile . After signing the Capitulation of Santa Fe ( 17 of April of 1492 ) he organized his expedition in search of the Far East by sailing West.
Capitulations of Santa Fe

There were several reasons why the Catholic Monarchs did not decide to support the Columbian project. Apart from the war in Granada, Columbus’s demands were exaggerated and the experts who analyzed the project determined that it was very risky. Some courtiers, such as Luis de Santángel and Francisco de Pinelo, convinced the kings of the need to compromise. When the war in Granada was coming to an end, Columbus was received by the monarchs in Santa Fe, and they expressed their intention to finance the company.
The result of the negotiation was collected in the Santa Fe capitulations, signed in April 1492 . In them a series of concessions were made to Columbus, but all conditional on the fact of the discovery. The fundamental points of this contract granted Columbus enormous privileges, such as the title of Admiral and Governor General of the lands to discover. He was also awarded ten percent of the commercial profits, apart from other economic advantages.
With some letters to the Great Khan and instructions to organize the navy, Columbus went to the port of Palos de la Frontera, which was chosen as a starting point because it had a good fleet and sailors experienced in Atlantic navigations.
Discovery of America
First trip

When the preparations were finished, about ninety men embarked on three ships: two caravels, the Pinta and the Niña, captained by the brothers Martín Alonso and Vicente Yáñez Pinzón , and a ship, the Santa María, in which Christopher Columbus was going. Most of the crew was from Palos; only fifteen expedition members were not Andalusian: ten Basques and five foreigners. No women, friars, or soldiers embarked, but royal officers did to look after the economic interests of the monarchs, and an interpreter of oriental languages.
About the crew that made up the Santa María it is specified:On the Nao Santa María the Admiral raised the royal flag of Castile and Aragon. In it, the bailiff of the Navy Diego Arana, Da’s first cousin, embarked with Christopher Columbus. Beatriz Enríquez, Rodrigo Sánchez de Segovia, inspector general or overseer for the Kings and Rodrigo Escobedo, royal clerk. The owner of the ship Juan de la Cosa was the master and the pilot Sancho Ruiz, also carrying on board the physicist of Moguer Master Alonso, the surgeon Master Juan and 40 other sailors.
The 2 of August of 1492 , Christopher Columbus ship commanded all his people, and the next day, before sunrise, left the port of Palos heading for the Canaries. All the details of the trip are found in an exceptional document, the Diario that Colón wrote, known for the copy made by Fray Bartolomé de las Casas .
On the journey there were some problems. The most important was the discontent of the crew at the distance from the coasts and the continuous presence of trade winds, which carried them directly to the west, fearing that they would not find favorable winds to return to the peninsula. But before the end of August, contrary winds appeared, thanks to which the spirits calmed down.
The problems reappeared when entering the calm zone, which, together with the absence of landmarks, once again showed the discontent of the sailors. Columbus came to think that he had surpassed Japan , and his problems increased when a general mutiny broke out that he was able to contain after he managed to convince his men that in a few days they would find land. Soon the winds picked up, sailing speeds picked up, and signs of being near the shore began to appear: some flocks of birds and wood floating in the sea.
The journey lasted thirty-three days. The three ships arrived on December of October of 1492 on the island of Guanahani, called by Columbus San Salvador now Watling Island ( the name given by the English in the eighteenth century ), in the Bahamas ), after the sailor Juan Rodríguez Bermejo, known as Rodrigo de Triana , gave the mandatory cry of “Earth!”, Earning the thousand maravedíes that King Fernando had promised to the first to see the coasts of Asia . The admiral went ashore with the royal notary, the chaplain, and the officers; then knelt down, thanked God and with great pomp he took possession of the island in the name of the Catholic Monarchs , while scattered groups of natives, naked and apparently harmless, gazed at the newcomers with curiosity. Columbus would write:They are so naive and so generous with what they have that no one would believe it if they hadn’t seen it. If someone wants something they own, they never say no; on the contrary, they invite you to share it and show as much affection as if your whole soul were in it (…)
The people he spoke to were later identified as the Taino Indians , an ethnic group that later disappeared. Before them, the astonishment of the navigators was considerable, because they spoke a completely unknown language and belonged to a race that did not resemble any of those described in the books of the explorers and ancient chroniclers, from Herodotus to Marco Polo . But it did not occur to anyone, of course, that these lands did not belong to Asia.
They soon began to recognize the island’s coastline and, believing themselves to be the Far East, set sail again in search of Cipango ( Japan ). They traveled the coasts of several Bahamas islands, Cuba and Haiti , which received the name of Hispaniola. While still maintaining relationships with the Indians, the Spanish were looking for spices, though instead they saw corn, canoes, hammocks, and tobacco for the first time.
Discovery of Cuba and Hispaniola
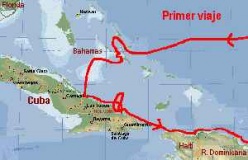
The 27 of October of 1492 arrives dusk to the north coast of the former province of Camagüey , and anchor their ships (discovery of Cuba). The next morning Columbus decides not to disembark in that area, and after waiting a while, he heads west, arriving in a few hours at a “mighty river”, which he wrote in his blog as “Rio de los Mares”.
It was in that place that Columbus stepped on Cuban soil. The dispute over where Columbus landed in Cuba is still valid, but many scholars on the subject affirm that it was because of Bariay . After the ceremony where he took possession of the land in the name of King Fernando, and named Cuba Juana , he sailed upstream by boat, where he later wrote:This is the most beautiful land that human eyes have ever seen.
Impatient Columbus to find gold, he set sail on December 12 , and passing through Punta de Maisí , he discovered Hispaniola ( Dominican Republic and Haiti ). On Christmas Eve 1492 the ship Santa María was wrecked on the north coast of Hispaniola. The cargo was saved thanks to the help of the natives, and with the remains of the ship Colón decided to build a fort, called La Navidad , which was the first Spanish settlement in America. There were 39 men left in order to maintain friendly relations with the islanders and to search for gold mines. On January 4, the Admiral gave the order to return. Along with the Spaniards, some indigenous people, parrots, turkeys, local products and exotic objects embarked. In the early days of navigation, Columbus wrote his famous Letter , which was intended to spread the news of his fabulous discovery.
Return
The difficulties of the return trip were enormous, but at all times Columbus demonstrated his magnificent seafaring qualities. The winds and storms separated the two boats, and Columbus, commanding the Girl, was forced to set sail for Lisbon , being received by Juan II, who was the first to hear the story of his adventure. The Portuguese king claimed his rights to the discovered lands, based on the Alcaçovas pact , but Columbus showed him that he had not gone to Guinea , but to the Indies. Fearing reprisals from the Catholic Monarchs, the monarch let him go to Palos.
Martín Alonso Pinzón, in command of the Pinta, had gotten lost in a storm and reached the coasts of Galicia , and from there he headed for Palos, where he arrived at the same time as Columbus, in mid-March. The Admiral set out to see the kings, who were in Barcelona. He crossed the peninsula arousing everyone’s curiosity with his spectacle of parrots, indigenous people, exotic feathers, etc., leaving the Spaniards impressed and admired.

The reception that Columbus had in Barcelona was great, and the kings confirmed all the privileges agreed in Santa Fe. They immediately began diplomatic contacts with the Pope to obtain the concession on the lands discovered and to be discovered, and with Portugal to establish a border in the discoveries, subject that caused tension between both kingdoms.
The starting point were two bulls awarded by Alexander VI. The first annexed the new lands to the Crown of Castile, and the second limited the area of expansion of the Portuguese and Castilians with a meridian located 100 leagues from the Azores. The negotiations were very tough and the Portuguese were not satisfied with the papal sanction, because, although they agreed that they should divide the world, they preferred that the dividing line be a parallel, since that is how they took over the southern hemisphere.
Finally, in June 1494, the problem was considered settled with the Treaty of Tordesillas, according to which both parties accepted that the demarcation line was the meridian located 370 leagues west of Cape Verde . The inaccuracies of the agreement and the difficulties in determining the length (which could only be achieved in the 18th century ), meant that the jurisdictional problems did not end. For this reason, the expansion of the Portuguese in Brazil and of the Spanish in Southeast Asia, with the conquest of the Philippine islands , would raise diplomatic problems among the monarchs of the Iberian Peninsula , which were resolved by the policy of force and the fait accompli .
Second trip
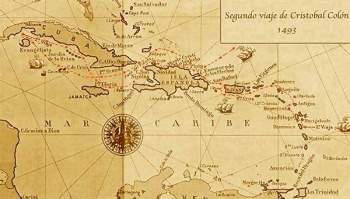
In September 1493 an Armada made up of 17 ships and a formidable force, close to 1,500 men, went to sea. Its objectives were to help the Spaniards who had remained in America during the first trip in the establishment of Fort Navidad, to continue the discoveries trying to reach the lands of the Great Khan , and to colonize the islands previously found. After a stopover in the Canary Islands , which over time would become something common in the Carrera de Indias, Colón ordered to head further south than on the first trip, thinking that in this way he would reach Cipango ( Japan ) more easily.
What Columbus found on this second voyage was, in fact, the fastest and safest route to sail to America. In just 21 days they managed to reach the Deseada and Dominica islands , and then discover Guadeloupe , Monserrat and Puerto Rico . On the north coast of Haiti , where Fort Navidad was located, Colón learned that the 39 men he had left on the first trip had been murdered, according to what he was told at the hands of the cacique Caonabó and his companions. The 6 as January as 1494 Columbus founded La Isabela in that place, the first Spanish town in America. From there he sent some expeditions in search of gold, of which he sent some samples to Spain, and proposed to the crown that it authorize the exchange of cattle and victuals for Carib Indian slaves. In April he moved to Cuba and shortly after to Jamaica .
Upon his return to La Isabela, Colón discovered that many discontents had left it, while diseases took hold of the remaining settlers and the indigenous people rebelled. After a short fight, Columbus imposed slavery on the defeated and paid a tribute in gold and cotton. Aware of the terrible situation in their new dominions, the Catholic Monarchs make the decision to send Juan de Aguado to inform them of what is happening. In March 1496 Aguado was returning to Spain, accompanied by Columbus, who did not want to lose the favor of the court for his discovery company. He left built six fortresses and the command of the territories granted to his brother. In the interview with the kings the following fall, Columbus received criticism for the conflict and the lack of profitability of his companies, but he justified himself with the evangelizing purpose.
Third travel
It takes Columbus three years to organize his next trip, while his prestige and that of the American company itself, which seems like a ruinous business, are declining at times. Of the eight ships that make up the Colombian flotilla this time, which left the peninsula in January 1498 , five went on to reinforce the establishments on Hispaniola, and three were dedicated to new discoveries. At the end of July, Columbus landed on the island of Trinidad and shortly afterwards explored the Venezuelan coast of Paria and the mouth of the great Orinoco River , where he considers that the earthly paradise had been located. In August 1498 he was back on Hispaniola.
From now on, the political and administrative conflicts completely absorb Colón, preventing him from continuing with the explorations. First he has to face an indigenous uprising and, later, the Spaniards themselves rebel, led by Francisco Roldán. Only the authorization of the distribution of the indigenous lands and the concession of their personal service to the Spaniards, together with some measures of force, managed to stop the revolt.
In 1500, a royal envoy arrived in Hispaniola, Francisco Bobadilla , who came as an investigating judge with full powers to put order in the colony. Bobadilla found Columbus guilty of all the evils, seized his house, papers and goods, opened a process for him and sent him to Spain loaded with shackles along with his brothers Diego and Bartolomé. He then gave freedom to take gold, sold land and distributed Indians. Thus ended the stage of personalist government in the New World and a new order began. Columbus arrived in Spain in November 1500. Although the kings ordered him to be released immediately, his enormous privileges had disappeared. Columbus had succeeded as a sailor and discoverer, but had failed as a ruler.
Fourth trip
In spite of everything, in March 1502 he received the task of preparing a fourth and final trip, the objective of which should be to find the strait that was believed to separate the mainland from the north and the south, to achieve free passage to the Asian continent. Columbus was prohibited from landing on Hispaniola to avoid conflicts, as well as the capture of slaves. Four caravels with 140 men were prepared, including the son of the discoverer, Hernando Colón, who left us an account of the trip.
In May 1502 they left the peninsula, heading for Martinique, Dominica, Hispaniola (despite the prohibition), Jamaica and Cuba. From there he sailed to the coast of Honduras , Nicaragua , Costa Rica and Panama , where he managed to rescue (trade) a certain amount of gold. In November they founded Portobelo and soon after, Nombre de Dios , also on the Panamanian coast. After suffering an indigenous attack they had to set sail for Cuba, but they were shipwrecked off Jamaica. Until then, the fourth Columbian trip had served to prove that from Brazil to Honduras there was no passage to the east. From Jamaica, Columbus dispatches seven of his men to call for help in Hispaniola (Santo Domingo). Finally, in July 1504 the castaways were rescued and in November of that year Columbus arrived, already very ill, in Spain.
Death
His final return to Spain took place on November 7, 1504. After unsuccessfully claiming his rights from King Ferdinand for two years, and already ill and tired, the admiral settled in a Franciscan convent. His hair was practically white, heavy lines crisscrossing his face, and deep dark circles around his eyes.

Saddened and melancholic, Colón sees his death near, dictating a will in favor of his children, brothers and Beatriz Enríquez de Harana, a woman with whom he shared part of his life and mother of his son Hernando. Christopher Columbus died without recognition, practically abandoned in a humble home in Valladolid , Spain on ( May 20 , 1506 ) suffering from gout and other diseases. There is also another version that says Colón enjoyed very good income in his last stage of life. Columbus dies without knowing that in his exploration he had found a continent unknown until then by the Europeans of his time and to which the name of America will be given , the result of a mistake when assigning its discovery to Americo Vespuccio .
Initially buried in Seville , his son Diego moved his remains years later to Hispaniola (Santo Domingo) in 1554 , of which he was governor. It is also said that in 1796 they were transferred to the Cathedral of Havana . The Cathedral of Seville also claims to have the remains of the Grand Admiral.
Popular culture
Movies
- Christopher Columbus ( 1949 ), according to his own label is the greatest adventure that a man has ever lived.
- 1492, the conquest of Paradise ( 1991 ) by director Ridley Scott is a film that tries to be as faithful as possible to historical facts. In the role of Columbus is the French actor Gérard Depardieu .
- Christopher Columbus: The Discovery ( 1991 ) with excellent actors such as Marlon Brando , Benicio del Toro , Catherine Zeta-Jones .
