Geometric Isomerism is the type of space isomerism, also known as stereoisomerism, which is characterized by presenting a pair of isomers with different three-dimensional dimensions. This happens due to the presence of different ligands.
Also known as cis-trans isomerism, it is only possible in open chains that have a double carbon bond, that is, in unsaturated open chains.
Geometric isomerism, however, does not only happen in open chains, it can also happen in cyclic compounds.
Cis and Trans
When the carbon binders of the chemical substance are structurally positioned on the same side, the isomerism is called cis .
When the carbon binders of the chemical substance are structurally positioned on the opposite side, the isomerism is called trans .
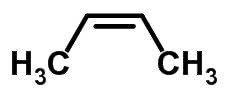
Molecular form of cis-but-2-ene C 4 H 8
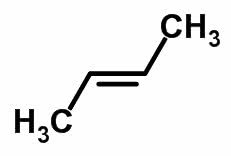
Molecular form of trans-but-2-ene C 4 H 8
Geometric Isomerism in Cyclic Compounds
In cyclic compounds, the binders must be different in at least two carbons.
In this case, cis and trans isomers can occur at the same time.
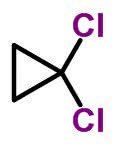
Molecular form of cis-dichlorocyclopropane C 3 H 4 Cl 2
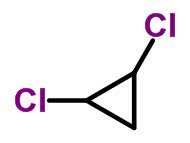
Molecular form of trans-dichlorocyclopropane C 3 H 4 Cl 2
Nomenclature
That is why the nomenclature of geometric isomers contains the prefix cis and trans in the name, which serves to identify the substances.
Cis and trans can be replaced by the initials Z and E , respectively. This is the nomenclature recommended by IUPAC (International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry).
That’s because Z, from the German zusammen , means “together”. And from German entegegen , it means “opposites”.
Exercises
1. (Fuvest) How many structural and geometric isomers, also considering the cyclic, are predicted with the molecular formula C 3 H 5 Cl?
a) 2.
b) 3.
c) 4.
d) 5.
e) 7.
Answer
Alternative d: 5
2. (Vunesp-SP) Presents geometric isomerism:
a) pent-2-ene
b) but-1,2-diene
c) propene
d) tetrabromo ethylene
e) 1,2-dimethyl benzene
Answer
Alternative to: pent-2-eno
3. (Vunesp-SP) Among the compounds
I. C 2 H 6 O.
II. C 3 H 6 O.
III. C 2 H 2 Cℓ 2 .
have geometric isomerism:
a) I, only.
b) II, only.
c) III, only.
d) I and II, only.
e) II and III, only.
Answer
Alternative c: III, only.
